The olives are another pair of swellings locatedlaterally to the pyramids between the ventrolateral and posterolateral sulci. When these pyramidal fibers are traced downward, it is found that some two-thirds or more of them leave the pyramids in successive bundles, and decussate in the anterior median fissure of the medulla oblongata, forming what is termed the pyramidal decussation. Furthermore, it appears that corticospinal fibres in monotreme mammals do not form a paramedian pyramid as they do in the rest of them. Corresponding portions of gray matter extend to these regions and are the nucleus gracilis and nucleus cuneatus respectively.
Revisions: 41. The Corticospinal tract (CST) controls afferent signals, spinal responses, and nerve cell activities, the most significant of which is the regulation of intentional distal motions. Signalling all along the corticospinal tract is associated with a variety of actions, including strolling and grasping, but it is particularly significant for fine finger gestures, such as typing, writing, or knitting garments. Unlike the anterior surface of the medulla, the posterior surface is largely obstructed from view and is relatively devoid of features. Complications involving Medullary Pyramids: Bilateral infarction in the medulla pyramids: Best CBD Cream for Alzheimers and Dementia, CBD vs. CBN Benefits, Differences, Potential Side Effects, CBD Oil vs CBN Oil for Sleep Benefits, Potency, Side Effects. As such, some of the information contained herein may be outdated. They will, nevertheless, be capable of wrinkling their brow because the corticobulbar tract innervates it bilaterally. These regulate somatic motor activity in the brain, such as the muscles that are involved in mastication, expressiveness, and movement of the eyes. At the highest point in the medulla, the anterior inferior cerebellar artery supplies the outermost portions of the posterior region. Countercurrent mechanisms are important in other aspects of physiological control, as well. Section of the medulla oblongata at the level of the decussation of the pyramids. The medulla houses essential ascending and descending nerve tracts as well as brainstem nuclei. Between the peduncle and the olivary nuclei resides the lateral spinothalamic tract and the more lateral anterior spinocerebellar tract. Conditions comorbid to autism spectrum disorders, British Journal of Developmental Psychology, British Journal of Educational Psychology, British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology, Human brain frontal (coronal) section description 2.JPG, anterior median fissure of the medulla oblongata, Anatomy Atlases - Microscopic Anatomy, plate 17.326. The vascular supply to the vagus and glossopharyngeal nerves is mainly repetitive due to their physical proximity. Some features are seen in all three cross sections. Secretion/absorption functions in various regions of the nephron in relationship to the gradient of osmolarity within the renal medulla. But opting out of some of these cookies may affect your browsing experience. Anterior surface. The medullary pyramids are located in the ventral region of the medulla oblongata. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the medulla its external features, internal anatomy, and blood supply. Quadriparesis is a sickness in which all four extremities are feeble (both legs and arms). 5). The medulla oblongata (medulla) is one of the three regions that make upthe brainstem. The posterior white matter contains the fasiculus gracilis and the more lateral fasiculus cuneatus. The anterior median fissure separates these two crest-shaped structures that run along the length of the medulla oblongata (Figure 1). The jugular branch of the ascending pharyngeal artery provides arterial supply at the region of the jugular ganglion, and this is where the nerve leaves the skull base via the pars venosa of the jugular foramen. Fibres that decussate migrate down the lateral corticospinal tract, whereas fibres (that do not decussate) move down the anterior corticospinal tract. Approximately ninety per cent of these fibres exit the pyramids in consecutive packages and cross over or decussate in the medulla oblongatas anterior median fissure as pyramidal decussation or motor decussation. As a result of the weakness on the left part of the tongue, the tongue is pushed forward by the powerful muscle on the right side. Below the level of the olives the posterior half of the medulla is supplied by the posterior spinal artery.
Centrally, the central canal can be seen as it rises to form the fourth ventricle in the final cross section. Trigeminal lemniscus (Dorsal trigeminal tract, Ventral trigeminal tract), cranial nuclei: GSA: Principal V/Spinal V - VIII-c (Dorsal, Anterior)/VIII-v (Lateral, Superior, Medial, Inferior) - SVE: Motor V - VII - GSE: VI - GVE: VII: Superior salivary nucleus, MLF, III, IV and VI (vestibulo-oculomotor fibers, medial vestibulospinal tract), sensory/ascending: Trapezoid body/VIII - Superior olivary nucleus, Inferior cerebellar peduncle (Vestibulocerebellar tract), motor/descending: Apneustic center Pneumotaxic center (Medial parabrachial nucleus) - Lateral parabrachial nucleus, Middle cerebellar peduncles (Pontocerebellar fibers) - Pontine nucleimotor/descending: Corticospinal tract - Corticobulbar tract - Corticopontine fibers, Reticular formation (Caudal, Oral, Tegmental, Paramedian) Raphe nuclei (Median), surface: Posterior median sulcus - Postero-lateral sulcus - Area postrema, cranial nuclei: GVA: VII,IX,X: Solitary/tract SVA: Gustatory nucleus GSE: XII GVE: IX,X,XI: Ambiguus SVE: X: Dorsal IX: Inferior salivatory nucleus - MLF, III, IV and VI, sensory/ascending: Gracile nucleus Cuneate nucleus (Accessory cuneate nucleus) Sensory decussation Medial lemniscus, motor/descending: Dorsal respiratory group, motor/descending: Ventral respiratory group - Pyramid (Motor decussation) - Inferior olivary nucleus (Olivocerebellar tract, Rubro-olivary tract)surface: Anterior median fissure - Antero-lateral sulcus - Arcuate nucleus of medulla - Olivary body, Reticular formation (Gigantocellular, Parvocellular, Ventral, Lateral, Paramedian) Raphe nuclei (Obscurus, Magnus, Pallidus). As described earlier, the loop of Henle is a tight hairpin loop that extends from the corticomedullary junction to the inner medulla. Figure 5: Cross-section of Medulla the Decussation of the Medial Lemniscus. This level marks thesensory decussation occurs of the medial lemniscus. The majority of the axons of the anterior corticospinal tract decussate in the spinal cord right before synapsing with lower motor nerve cells. Motor quadriplegia can develop from a bilateral infarction in the medulla pyramids. As we move lateralfrom the midline, the fasciculus gracilis and fasciculus cuneatus are seen, separated by the posterior intermediate sulcus.  The corticospinal tracts are located in the pyramids area. We use cookies to improve your experience on our site and to show you relevant advertising. An additional cranial nucleus comes into view lateral to the hypoglossal - the dorsal vagal nucleus. Psychology Wiki is a FANDOM Lifestyle Community. Out of these, the cookies that are categorized as necessary are stored on your browser as they are essential for the working of basic functionalities of the website. The corticobulbar tract is a downward channel that runs parallel to the corticospinal tract and innervates multiple cranial nerves (Figure 2). These pyramid wounds are typically caused by an occiput or spinal level C1 displacement. The motor fibres that travel from the brain to the medulla oblongata and spinal cord are housed in the two pyramids. When the fibres intersect, the pyramids lowest limit is defined (decussate). Scheme showing passage of various fasciculi from medulla spinalis to medulla oblongata. Water now reenters the blood within the ascending loop and NaCl and urea leave.
The corticospinal tracts are located in the pyramids area. We use cookies to improve your experience on our site and to show you relevant advertising. An additional cranial nucleus comes into view lateral to the hypoglossal - the dorsal vagal nucleus. Psychology Wiki is a FANDOM Lifestyle Community. Out of these, the cookies that are categorized as necessary are stored on your browser as they are essential for the working of basic functionalities of the website. The corticobulbar tract is a downward channel that runs parallel to the corticospinal tract and innervates multiple cranial nerves (Figure 2). These pyramid wounds are typically caused by an occiput or spinal level C1 displacement. The motor fibres that travel from the brain to the medulla oblongata and spinal cord are housed in the two pyramids. When the fibres intersect, the pyramids lowest limit is defined (decussate). Scheme showing passage of various fasciculi from medulla spinalis to medulla oblongata. Water now reenters the blood within the ascending loop and NaCl and urea leave.
Best CBD Cream for Alzheimers & Dementia. The corticobulbar tracts emerge from the internal capsule as many bundles and join the basilar region of the pons. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. Stevens & Lowe's Human Histology (Fourth Edition), Projections from the Brain to the Spinal Cord, Because the corticospinal fibers form the, Practical Surgical Neuropathology: A Diagnostic Approach (Second Edition), The vagus nerve exits the medulla oblongata between the, Lapresle & Lasjaunias, 1986; Lasjaunias & Berenstein, 1987; Leblanc, 2000, Familial Hypophosphatemia and Related Disorders, Soft-tissue calcification, particularly at the level of the renal, Nathan et al., 1990; Galea and Darian-Smith, 1994, Nathan and Smith, 1955; Yakovlev and Rakic, 1966, Nakanishi et al., 2004; Souma et al., 2009, Wassermann et al., 1991; Bawa et al., 2004, Eyre et al., 2000; ten Donkelaar et al., 2004; Eyre, 2007, Animal Models for the Study of Human Disease (Second Edition), Comparing porcine and human kidneys, anatomic similarities include an undivided renal cortex, multiple, A key element in urine formation is the gradient of osmolality present in the renal.
Original Author(s): Luke Peters Last updated: June 8, 2021 (Pyramid Pyramis medullae oblongatae; Pyramis bulbi). There are several structures visible on the anterior surface of the medulla - namely thethree fissures/sulci, the pyramids, the olives, and five cranial nerves. The large inferior olivary nucleus is responsible for the external expansion of the olives. Extrapyramidal tracts are motor tracts that do not pass via the medullary pyramids.
The anterior median fissure separates these two crest-shaped structures that run along the length of the medulla oblongata. The medullary pyramids are located in the ventral region of the medulla oblongata. 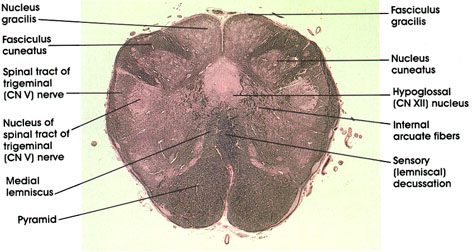
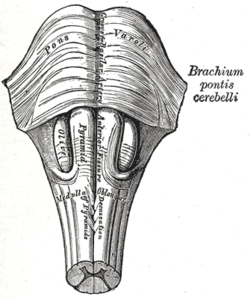 When the top nerve cells of the corticospinal tract are injured, it can result in a group of impairments known as upper motor nerve cell syndrome. The remaining portions are supplied by the posterior inferior cerebellar and vertebral arteries.
When the top nerve cells of the corticospinal tract are injured, it can result in a group of impairments known as upper motor nerve cell syndrome. The remaining portions are supplied by the posterior inferior cerebellar and vertebral arteries.  As we move away from the midline, two sulci are visible the ventrolateral sulcus and the posterolateral sulcus. Ventral view. Above, the sulcus ends at the point in which the fourth ventricle develops. The lower face muscles get contralateral information from the opposite motor cortex via the facial nucleus (VII). The internal structures of the medulla must be viewed in cross section to understand the layout. The corticobulbar tracts emerge from the internal capsule as many bundles and join the basilar region of the pons. This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. A person with quadriparesis can still move and sense their extremities. The decussated fibres form the lateral corticospinal tract; these would join the spinal cord and induce motion on the part of the body that is contralateral to the hemisphere from which they arose. Template:Infobox Brain
As we move away from the midline, two sulci are visible the ventrolateral sulcus and the posterolateral sulcus. Ventral view. Above, the sulcus ends at the point in which the fourth ventricle develops. The lower face muscles get contralateral information from the opposite motor cortex via the facial nucleus (VII). The internal structures of the medulla must be viewed in cross section to understand the layout. The corticobulbar tracts emerge from the internal capsule as many bundles and join the basilar region of the pons. This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. A person with quadriparesis can still move and sense their extremities. The decussated fibres form the lateral corticospinal tract; these would join the spinal cord and induce motion on the part of the body that is contralateral to the hemisphere from which they arose. Template:Infobox Brain
About ninety per cent of the fibres in the corticospinal tract decussate, or crossover over to the opposite side of the brainstem, near the foot of the pyramids in a tangle of axons known as the pyramidal decussation. They continue to do so as the medulla ascends. Please edit the article if this is the case, and feel free to remove this notice when it is no longer relevant. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions. This occurs just as the medulla exits the skull through the foramen magnum.
Moving further lateral, the nucleus of tractus solitarius comes into view. Centrally, the medial lemniscus hugs the midline posterior to the pyramids, as does the tectospinal tract. The remaining ten per cent of fibres in the anterior corticospinal tract remain uncrossed. As blood flows down the loop, water leaves and NaCl and urea enter the blood, but as the blood passes the tip of the loop, the situation becomes reversed. In the posteriolateral sulcus, three more cranial nerves join the medulla (CN IX, CN X, and CN XI). Quadriplegia impacts the human body from the neck down, reducing a persons freedom severely. The following attempts to simplify this complexity.
End on alpha nerve cells or interneurons that innervate alpha nerve cells in the brainstem. Upper nerve cells are the nerve cells that move along the corticospinal tract; they synapse on lower motor nerve cells in the spinal cord, which communicate directly with skeletal muscle to generate muscular contraction. Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. Superficial dissection of brain-stem. The medullary pyramids are two white matter formations in the medulla oblongata of the brainstem that carry motor fibres from the corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts, which are commonly understood as the pyramidal tracts. Found an error? The artery for the medulla oblongatas lateral fossula gives birth to arterioles that supply the vagus nerve roots. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the medulla - its external features, internal anatomy, and blood supply. A similar mechanism operates in the feet and legs of aquatic birds to prevent them from losing valuable body heat while they are swimming in freezing water. Extrapyramidal tracts are motor tracts that do not traverse the thalamus. In this article, the role of the medullary pyramids and their structural significance concerning motor functions of the brain will be discussed and explained. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter this site.
The artery for the medulla oblongatas lateral fossula gives birth to arterioles that supply the vagus nerve roots. Now a much smaller structure, the trigeminal tract and nucleus is seen adjacent to the peduncle. Copyright 2022 Elsevier B.V. or its licensors or contributors. Figure 6: Cross-section of the Medulla at the level of the Olives. Axons that innervate motor nerve cranial nuclei can decussate (cross) before terminating, causing them to innervate contralateral muscles. Also, there is a noticeable protrusion termed as olive on the side of every pyramid.
Bruce M. Carlson MD, PhD, in The Human Body, 2019. Figure 1 The three major parts of the brainstem.
The behind of pyramids on the medulla oblongata is present the fibres of the posterior column that carry sensory and proprioceptive input.
Trauma caused by an automobile collision can lead to brainstem damage affecting the pyramids of the medulla oblongata.
Information on the pyramids can be found here. Decussation of pyramids. With water entering the system, one would expect that it would dilute the concentration gradient, causing it ultimately to disappear. Section of the medulla oblongata at the level of the decussation of the pyramids. Different parts of the brain are responsible for various tasks that need to be performed correctly to ensure the working and functioning of a healthy body. The pyramids are paired swellings found between the anterior median fissure and the ventrolateral sulcus. The large trigeminal nucleus and tracts can be found posterior to these tracts. The corticospinal tracts are located in the pyramids area. This is a continuation of the substantia gelatinosa of the spinal cord. The nucleus ambiguous remains as it was previously, while the hypoglossal nucleus has migrated with the central canal posteriorly, joined by the medial longitudinal fasciulus. Medial medullary infarcts result in less than one per cent of vertebrobasilar strokes and are seldom bilateral. The corticobulbar and corticospinal pathways are motor fibres found in the medullary pyramids. To find out more, read our privacy policy. The weakening could be either transient or lifelong. Lateral to the medial lemniscus, the trigeminal nucleus and spinal tract can once again be seen, as can thespinocerebellar tracts and the lateral spinothalamic tract. Level of Decussation of the Medial Lemniscus, Level of decussation of the medial lemnisci, Access over 1700 multiple choice questions. Extrapyramidal tracts are motor tracts that do not traverse the thalamus. Any cookies that may not be particularly necessary for the website to function and is used specifically to collect user personal data via analytics, ads, other embedded contents are termed as non-necessary cookies. The corticobulbar tract innervates the nuclei of the cranial nerves directly: Cranial nerves motor areas of X in the nucleus ambiguus. Ventral view. Tetraparesis is another name for it. As a consequence, a lesion affecting the right motor cortex/internal capsule would cause weakness in the left hypoglossal muscle.
Having crossed the middle line, they pass down in the posterior part of the lateral funiculus as the lateral cerebrospinal fasciculus. The anterior median fissure separates these two crest-shaped structures that run along the length of the medulla oblongata. The formation and maintenance of this gradient is the result of a countercurrent mechanism that involves both the loop of Henle and its accompanying vasculature.
A few complications that arise from injury to the spinal cord or brainstem will also be mentioned. After crossing the middle line, the lateral corticospinal tract descends into the lateral funiculus as the lateral corticospinal tract. As we move away from the midline, two sulci are visible - the ventrolateral sulcus and the posterolateral sulcus. In human beings, it shows the actual highest order of motor function and is most effective in the control of precise, digital motions. Having crossed the middle line, they pass down in the posterior part of the lateral funiculus as the lateral cerebrospinal fasciculus. g) (Sachs,1994). Both the loop of Henle and the vasa recta work in concert to maintain the osmotic gradient. After spinal cord damage, both voluntary (sensory-motor) and unintentional control can be compromised, with the degree of restoration varying according to the seriousness of the lesion. Best Nootropic Stacking Strategy for Brain Power. Scheme showing passage of various fasciculi from medulla spinalis to medulla oblongata. The medullary pyramids are located in the ventral region of the medulla oblongata. Similar to the anterior surface, the posterior surface has a midline structure - the posterior median sulcus - which is continuous below as the posterior median sulcus of the spinal cord. Above, the sulcus ends at the point in which the fourth ventricle develops. The related medial and dorsal accessory olivary nuclei can be seen medial and posterior to this structure respectively. Accompanying the loop is a similar hairpin-looped vascular configuration, called the vasa recta. The corticobulbar and corticospinal pathways are motor fibres found in the medullary pyramids. Each has an anterolateral sulcus along its lateral wall, from which the hypoglossal nerve exits. Throughout the medulla, the anterior spinal artery supplies a region beginning at the central canal (or anterior border of the fourth ventricle), and fans out to encompass the pyramids. Figure 7: Blood Supply to the Medulla at: Decussation of Pyramids, Decussation of the Lemnisci, and at the level of the olives. In the midline of the medulla isthe anterior median fissure,which is continuous along the length of the spinal cord. This website uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website. Anteriorly we can see the paired lumps representing the pyramids which are separated by the anterior median fissure. anterior median fissure of the medulla oblongata, https://www.wikidoc.org/index.php?title=Decussation_of_the_pyramids&oldid=672417, Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License, This page was last edited 00:31, 9 August 2012 by wikidoc user. Unchanged from the spinal cord, the spinocerebellar tracts (posterior and anterior) are locatedlaterally, with the lateral spinothalamic tract situatedbetween them. The fibres can go in a variety of directions and terminate in a variety of ways: The cranial nerves innervate the facial muscles, tongue, muscles of the jaw, and muscles of the pharynx. These rules, however, have two exceptions: Since corticospinal fibres produce the medullary pyramids in mammals, it has been referred to as the pyramidal tract. The use of such a phrase may generate some misunderstanding because the cells of derivation are, by chance, pyramidal nerve cells in the cerebral cortex. Corticospinal axons decussate (or intersect over) the central line and proceed down the spinal cord on the contralateral area at the pyramids most caudal end. 13.9).