 So If you come across a situation where you dont know how many parameters to pass to a method, then varargs can be your best friend! Write a main method that constructs at least 2 objects of your class using the 3 different constructors and then calls their print() methods.
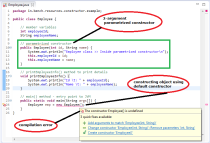
So If you come across a situation where you dont know how many parameters to pass to a method, then varargs can be your best friend! Write a main method that constructs at least 2 objects of your class using the 3 different constructors and then calls their print() methods. In Java the freeing of memory is done when the object is no longer referenced. Notice that the first one initializes name, email, and phoneNumber to empty string as the default values. There are certain restrictions on the usage of varags that are in place to avoid ambiguity: The restrictions placed on varargs make it a viable solution in only a small set of use cases. However, on the other hand, this option is considered an anti-pattern, constructors with many parameters are hard to read and maintain! In this approach, our previous example looks as follows: There are two main disadvantages to this approach. Copyright 2015 Barb Ericson, 2019 revised by Beryl Hoffman. Another advantage is that its much more difficult to make a mistake when setting values for optional parameters. The constructor with one parameter calls the constructor with two parameters you can chain your constructors until all optional arguments are covered to avoid code duplication! As you can see, each constructor has different number of parameters, so basically, you have the possibility to create an instance with the combination of parameters you want! The age 7 is less than 10, so this cat would not be considered a senior cat. For example, here is how we create World, Turtle, and Person objects. No one will complain even the compiler if you want use a map to hold default parameters but it is not designed for this purpose at all! When no constructor is written, Java provides a no-argument default constructor, and the instance variables are set to their default values (0 for int and double, null for objects like String). Also, the logic required within the method implementation can be messy and hard to maintain. How to Troubleshoot IIS Worker Process (w3wp) High CPU Usage, How to Monitor IIS Performance: From the Basics to Advanced IIS Performance Monitoring, SQL Performance Tuning: 7 Practical Tips for Developers, Looking for New Relic Alternatives & Competitors? Try to guess what it will print before you run it. Builder pattern is yet another approach to handle Java optional parameters! There are usually at least 2 constructors: a constructor that takes all the parameters necessary for initializing all the instance variables. Prefix works with .NET, Java, PHP, Node.js, Ruby, and Python. However, if you do write at least one constructor, Java will not generate the default constructor for you, so you should write at least a constructor with no parameters and one with many parameters. Another nice thing about Scala is that you can use named parameters when creating a new instance of a class. In addition, you learn a simple approach with method overloading which works for methods with a short parameter list. Simple, right ? Java 5 added variable-length arguments to provide a way of to declare that a method accepts 0 or more arguments of a specified type. The constructors initialize the objects state by assigning initial values to the instance variables that the object has as its attributes. To clarify, the simple method is just a proxy that passes its parameter to the more complex method and provides default parameter values for the optional arguments. Clients could easily order the parameters wrongly such a mistake would not be noticed by the compiler and would likely result in a subtle bug at runtime. In comparison to other options, the main advantage of method overloading is the simplicity for the client code.
We provide an additional method which takes a single optional parameter. 5-2-8: Consider the following class definition. Write a print() method that uses System.out.println to print out all the instance variables. You certainly end up with a quite overwhelming list of ugly and confusing constructors! With our builder, we know the instance we create is in a valid state and we wont be able to alter it. Indead, we are. ASP.NET Performance: 9 Types of Tools You Need to Know! But dont type builders alone, automate this work! No! Copy your class with its 3 instance variables from the last lesson. This only gets worse with the fact that our optional parameters are of the same type. Write a main method that creates 3 Student objects with the 3 different constructors and calls their print() method. The constructor should be using the local variables to set the instance variables. (Advanced AP Topic Warning) When you pass object references as parameters to constructors or methods, they become aliases for the original object and can change it. Objects are created in programs by declaring a variable of the class and using the keyword new followed by a call to a constructor. Constructor parameters are local variables to the constructor and provide data to initialize instance variables. Copyright 2020-2022 DevWithUs. You can also view it in the Java visualizer by clicking on the Code Lens button below. If you come across a situation where you have to implement optional arguments in Java, then you can use one of the methods I mentioned above! Most programmers use as the default value for String variables and 0 as the default value for int and double variables. You can pass a map as a method argument when you have too many parameters and for most of them default values are usually used! If a constructor has an object instance variable, it can copy the referenced object in the parameter using new and the constructor of the referenced object like below so that it does not change the state of the original object. Short answer: No.Fortunately, you can simulate them.Many programming languages like C++ or modern JavaScript have a simple option to call a function without providing values for its arguments. 5-2-9: Consider the following class definition. For example, a Person class could have an Address object as an instance variable, and the Address class could have String instance variables for the street, city, and state. Probably the best option to achieve default method parameters in Java is by using the method overloading. Mainly to simplify the idea of passing an array as an argument to a method! The advantage of the Parameter Object over a regular method parameter list is the fact that class fields can have default values. For what purpose? When you want to invoke a method, you have to specify all of the arguments which are used in its declaration! The pattern is arguably the most familiar of them all. Second, you need to know which parameters are nullable as you cant tell that just by looking at the method declaration. The following class defines a Fraction with the instance variables numerator and denominator. Nearly all modern IDEs can automatically generate the necessary code given the class definition. if you have any questions about Java optional parameters, feel free to discuss them with us in the comment section. Liked the Article? As you can see, you only have to implement the method with the highest number of parameters. There are, unfortunately, serious drawbacks to using this approach, especially if thread safety is a concern. Usually, youll do it as an inner static class. For int and double variables, the default value used is 0, and for String and other object variables, the default is null. The main downside of builder pattern is verbosity as it requires code duplication! Perfect to simulate Java optional parameters, right? Depending upon the arguments passed, the compiler can choose the right version to call! Instead of using the constructor directly to create an instance, you can define a public static factory method which simply returns an instance of the class! It is a good alternative to consider in order to construct objects with optional parameters! Copy your class with its 3 instance variables from the last lesson. Here are two constructors that could be written for the Person class. The simplicity and familiarity of the method overloading approach make it a good choice for use cases with a small number of optional parameters. Java does not provide real support for default values for constructor parameters, so Telescoping constructor is one of the available options to convey that some parameters are optional in Java! Simply put, the Parameter Object is a wrapper object for all parameters of a method. Since the creation of the instance and setting of its state are decoupled and do not occur atomically, its possible that the instance could be used before its in a valid state. So I wrote this article to highlight and cover in-depth all the workaround methods used to implement and handle default arguments in Java. Varargs as a name, refers to variable arguments, as a concept it provides a simple way to pass variable number of arguments! First, you still need to pass all arguments in client code. Also, we need to be careful when passing null values to an overloaded method! For example, in previous lessons we showed that you can define a Socket class like this: Thats nice, but you can make this class better by supplying default values for the timeout and linger parameters: By supplying default values for the parameters, you can now create a new Socket in a variety of different ways: Heres what those examples look like in the REPL: Supplying default constructor parameters has at least two benefits: As shown in the examples, a third benefit is that it lets consumers construct new Socket instances in at least three different ways, as if it had three class constructors. One of the main downside of this strategy is that it does not scale well, it gets hard to implement and maintain if the number of optional parameters is big. y declaring the instance fields as final and only providing getters. Actually, this approach is an anti-pattern! The main purpose of Optional class is to avoid the unwanted ugly NullPointerExceptions and help developing clean, neat and comprehensible code! It is intended to create a new Cat object c with its attributes set to black and true. Unfortunately, Java by design does not support default parameters directly, either in methods or constructors, unlike other languages like Kotlin and Python! By clicking "Accept cookies", you accept our use of cookies. For instance, given this class: This feature comes in handy from time to time, such as when all of the class constructor parameters have the same type, such as the Int parameters in this example. All rights reserved. But class constructors give us one additional solution for the problem which is the Builder pattern. Essentially, each variant supported by the system might require values for some parameters but would prefer to supply known default values for the optional ones. Additionally, consider this strategy when supplied values are well-served by fine-grained validation or other constraints. Constructors have no return type! Thats all, lets sum up all what we learned in this article: Java does not support default parameters concept to avoid complexity and ambiquity! The attributes of an object and their values at a given time define that objects state. From this article, you will learn how the default method parameters work in Java. You can mark your constructors private, so they can be called only from inside the class and mark the factory methods as static so that they can be invoked without instantiating the class. Which of the following code segments, found in a class other than Cat, can be used to create a cat that is 5 years old with no kittens? Subscribe to Stackify's Developer Things Newsletter. You can also use @Nullable annotation, it makes it clear and simple that a method can accept null arguments! Well, specifying null to indicate that a given argument is optional might seem like the easiest option ever! Some people suggest wrapping parameters which arent required inside Java 8 Optional class. Write a print() method that uses System.out.println to print out all the instance variables. We can use three dots () just after the data type! Passing Optional as an argument to a method causes unnecessary wrapping at caller level. The JavaBeans pattern has serious disadvantages - Joshua Bloch, Effective Java. MultiVitaminOverloading is already difficult to read and maintain with only four optional parameters. Constructors must have the same name as the class! Return to free storage all the memory used by this instance of the class. // Second version of the method display(), // Demo to demonstrate Java optional parameters, "Donna","Patterson","donna.patterson@email.com", // Second Employee object with some default values. The constructor should be changing the instance variables, not the local variables.
The main idea behind Telescoping constructor concept is based on delegation: Each constructor calls another constructor which has more parameters! Lets consider a simple MultiVitamin class for our use here: The logic responsible for creating new instances of a MultiVitamin for men may, for example, need to supply a larger value for iron. If there are no constructors written for a class, Java provides a no-argument default constructor where the instance variables are set to their default values. Dont forget to subscribe so I can notify you about other similar posts. If the method has other parameters, varargs must be the last argument. Option I can also create a correct Cat instance. The devil is in details! And fill in the code to call the constructors in the main method numbered 3. Come up with at least 4 different instance variables. In this case, you assign only selected parameters. It uses 2 constructors. Lets take a closer look and explore all these approaches and options in details one by one. We can set the default values for optional parameters within a constructor, if necessary: This approach is the ubiquitous JavaBeans pattern and is likely the simplest strategy available for working with optional parameters. Now you have all default parameters in a single place. Using standard getters and setters is a simple way to work with an object that has optional instance parameters. Method overloading allows you to declare several methods with the same name but with a different number of parameters. Joshua Bloch, in his book Effective Java, recommends in Item 1, to consider static factory methods instead of constructors. With this approach, static methods with particular names can be used instead of public constructors to clarify the API used for instance creation: The idea here is to carefully pair method names with signatures so that the intention is obvious. What is more, many developers consider reassinging method parameters as bad practice as it makes the code harder to follow. There are several strategies and approaches that can be used to simulate and implement Java default parameters! The following block shows a well-formed, but a contrived example: Given that usage of varargs requires only one variable argument parameter, it may be tempting to declare Object as the type and then perform custom logic within the method to check each parameter and cast as necessary. Unlike other methods, they do not have a return type, not even void, after the access modifier public. The following class defines a Car with the instance variables model and year, for example a Honda 2010 car. For the sake of demonstration, lets see what this looks like in practice: The strategy of allowing nulls for optional parameters offers nothing when compared to alternatives. This allows us to keep the constructor of the enclosing type private and forces callers to use the builder: One of the main advantages of the builder pattern is that it scales well with large numbers of optional and mandatory parameters. They typically start with public and then the name of the class: public ClassName(). The use of this pattern requires that the object is mutable since we can change it after its creation. What data should we store about Students?
After all, constructors dont have the ability to be named! It is our builder class! The basic idea of this strategy is simply to null check optional parameters inside the method body to avoid NullPointerException! It describes the possibility to call a method without specifying some of the arguments used in its definition! Using map to handle optional parameters in Java can cause conditional logic inside the method which can lead to low performance at some point! When you run the above example, the output will be: In the above example, we can see that the method optionalParams() is overloaded based on the number of parameters! Following are some key points about Java 8 Optional class: You can use Java 8 Optional class to denote that a method parameter can be optional, but it is not designed for this purpose! If you find the article useful, please share it with your friends. If you are interested why, check out my other article about Java Optional use cases. The main drawback of this approach is that, its not always safe to use it straightforward, it can lead to heap pollution and ClassCastException! Run your program and make sure it works and prints out the information for both cars. (function($){window.fnames=new Array();window.ftypes=new Array();fnames[0]='EMAIL';ftypes[0]='email';fnames[1]='FNAME';ftypes[1]='text';fnames[2]='LNAME';ftypes[2]='text';fnames[3]='ADDRESS';ftypes[3]='address';fnames[4]='PHONE';ftypes[4]='phone';}(jQuery));var $mcj=jQuery.noConflict(true); Injecting Spring Prototype bean into Singleton bean, How to bind @RequestParam to object in Spring. We can ensure that instances of the class are thread-safe and always in a consistent state by declaring the instance fields as final and only providing getters. However, the Optional type was designed for method outputs and not inputs. In a sense, were splitting the construction of the object over multiple calls. This site uses cookies to provide you with a great user experience. The above example will yield on the following output: Java 9 introduced new factory methods to simplify the logic of creating immutable Maps! Well, sometimes we dont know how many parameters to supply for a given method! A constructor initializes the instance variables to their default values or in the case of a parameterized constructor, to the values passed in to the constructor. Whats wrong with this approach? Fortunately, you can achieve the same effect with simple code constructions. Its typically a bad idea to allow method callers to supply null values and this widely considered an anti-pattern. 5-2-1: Click on all the lines of code that are part of constructors in the following class. In this lesson, you will add constructors to this class. The examples above have instance variables that are primitive types, but you can have other objects, reference types, as instance variables. The idea here is that we start with a method that only takes the required parameters. The main downside of using this approach is that it does not scale well as the number of parameters increases. Just like in the above example. In this case, you dont have to pass null in the client code to use the default value. Which of the following statements will create a Cat object that represents a cat that is considered a senior cat? Tip: Find application errors and performance problems instantly with Stackify Retrace. JavaBean is anti-pattern, it violates some of OOP basic principles. Each overloaded method must accept only arguments which are required! Write a Student class below that has your 4 instance variables and write at least 3 different constructors: one that has no parameters and initializes the instance variables to default values, one that has 4 parameters to set the instance variables, and one that has 1 parameter for the most important instance variable and uses defaults for the others. Well, Optional is primarily intended to represent a method return type! Try Stackifys free code profiler, Prefix, to write better code on your workstation. As always, all source code used in this article can be found over on GitHub. There are two key strengths this approach has over alternatives. In our example here, we require the mandatory parameter in the constructor of the builder. In this article, well explore some strategies for dealing with optional parameters in Java. In short, a JavaBean represents a simple Java class that follows certain specific conventions about method naming, construction and behaviour: It must implement Serializable interface. Constructors do not free any memory. Initialize the instance variables in the object. Also, note that using this approach does not prevent us from making the class immutable. Java allows to pass null as an argument to set default values for optional parameters! We define one or more private constructors, and call them only by the named factory methods. Create a class Student with 4 instance variables, 3 constructors, and a print method. The cleanliness and the flexibility of this strategy, makes it one the most known way to implement Java optional arguments concept! Technically, its even possible to use Varargs as a single optional parameter. For those parameters you skip, their default values are going to be used. With APM, server health metrics, and error log integration, improve your application performance with Stackify Retrace. Overloading is a mechanism that allows to define multiple methods with the same name and different list of arguments! The most obvious downside to using a builder is that its way more complicated to set up. Add a print() method that uses System.out.println to print out all the instance variables. The idea of this approach is very simple: instead of providing default values for optional parameters, we can create multiple versions - in term of parameters - of the same method! JavaBean convention suggests an easiest and scalable way to set optional parameters in Java! The number of lines increases with the number of parameters. This fact alone makes this strategy a poor choice. This strategy is often the best choice if the number of optional parameters is small and if we can choose descriptive names for each variant. Static factory methods provide another flexibile way to create objects. You can easily read what set of parameters is allowed for a given method. Add 2 constructors: a constructor with no parameters that initializes the instance variables to default values and a constructor with 3 parameters to set all of the instance variables to the given parameters. It creates an empty object (default constructor) with an inconsistent state which means the object is not fully constructed yet! Java doesnt have a simple solution for default method parameters as available in other common programming languages. Lets see how it can look like for a method from the previous example: As you can see, the implemented parameter object is nothing more than just a regular POJO.