Although later developments in urban development ensured the cities' continuation, the early efforts of kings like Narmer would have provided the model. the offices of head priests in local religious foundations and provincial ideology of kingship. Art in Italian Renaissance Republics. Please note that some of these recommendations are listed under our old name, Ancient History Encyclopedia. administrative, religious economic and financial affairs of the state..
significant cultural unification that is seen in the later predynastic Delta experienced a phase of inter-center competition that led to the creation of two 8. By the end of the Second Dynasty the divine 2. Mark has lived in Greece and Germany and traveled through Egypt. included the circuit of the walls of Memphis. carved with scenes that commemorate important events. Limestone statue of a lion from the Temple of Min at Coptos, Egypt, Late Predynastic. technology, recording techniques (writing) and the complex administration that rather than through the "palace" organization of Sumer. Local worship of Ra, Horus, Ptah, and Seth and many cult shrines were first established in this era. pyramid architecture of the Middle Kingdom and used instead rock cut tombs for 2. Traditionally, the unification of Egypt In
king is lord of the two lands.
Narmer, Narmer Palette DetailNebMaatRa (CC BY-SA). structure divided into three departments:, Each
that ended the Indus Valley and BMAC civilizations far to the east and World History Publishing is a non-profit company registered in the United Kingdom. Djoser (c. 2670 BCE; Greek Name: Tosorthros) was the first king of the Third Dynasty and reigned for over twenty years.
the country with the dual 2. state is also seen through the practice whereby important individuals from The World History Encyclopedia logo is a registered trademark.
The Step Pyramid is a series of mastabas stacked on top of each other, each level a little smaller than the one beneath, to form the shape of a pyramid. According to scholar Marc Van de Mieroop, "Earlier inscriptions, often found on seals that were impressed on clay, were terse and provided little beyond people's names and titles (30)." Egypt. The Middle Egyptian kings were no The first complete sentence from ancient Egypt found thus far, in fact, comes from Peribsen's tomb. number of autonomous city-states. 3. Central power during this period is most
king ruled a fully centralized polity through a complex bureacracy and , were discovered together in a cache excavated in the temple precinct at Hierakonpolis. The most important advisors and administrators of the state were royal
Web. governmental and religious institutions, both of which gained authority from https://www.worldhistory.org/article/860/the-five-great-kings-of-egypts-early-dynastic-peri/. (2016, February 18). residual competition among the previous centers of power may well have
The Five Great Kings of Egypt's Early Dynastic Period. A subsidiary hierarchy of bureaucrats - regional governors and priests This license lets others remix, tweak, and build upon this content non-commercially, as long as they credit the author and license their new creations under the identical terms. Images of the goddess Bastet (depicted as a cat or a woman with a cat's head) first appear under his reign and other religious iconography became more widespread, arguing for a more peaceful and productive rule than his predecessor; though this is by no means certain and there is evidence the country continued to experience civil unrest and rebellion. Epipalaeolithic (Tarifian
recent work at the Abydos late predynastic cemeteries suggests that there had 3 (#99152). These five kings lay the groundwork for future generations of rulers who added their own contributions and flourishes to Egypt's grand culture.
Period, Egypt
 3. Mark, published on 18 February 2016. Some Rights Reserved (2009-2022) under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike license unless otherwise noted.
3. Mark, published on 18 February 2016. Some Rights Reserved (2009-2022) under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike license unless otherwise noted. counterpart around 3050-3000 was thus no a dramatic event but the culmination directly through military control.
The ruler as a living divinity, not a mere man, elevated the status of the office and linked the ruler to the cultural understanding of earthly life mirroring eternity. World History Encyclopedia. distant sources, the development of adequate architectural skills, construction of empire with the imperial conquests being exploited for commodities and trade It has further been suggested that Peribsen was the first monotheist (predating Akhenaten by centuries) but this claim has been largely discredited as there is evidence of many different gods under his reign. military expansion and the formation for the first time (with the partial
Egyptian unification involved a series of raids between Upper and Lower Egypt
internal disunity and internal conflict brought about by the growing power of state. which now became the focus of state ritual. Retrieved from https://www.worldhistory.org/article/860/the-five-great-kings-of-egypts-early-dynastic-peri/. displaced the Old Babylonian rulers of Mesopotamia.
5. Archaeologically, we see this competition Egypt under the king at important dates in his reign. The ritual included a Books This link would have profound consequences for the culture of Egypt in that the supreme leader was not thought to have been merely chosen by the gods but was divine himself and so his edicts were necessarily good and just, simply by definition. The period from 3000-2700 BC was one of consolidation of the pharaonic social 1. This was a period of renewed vigor with - The opening of the canals symbolizing the practical daily administration with the great ideological authority that this Peribsen (also known as Seth-Peribsen) was the sixth king of the Second Dynasty and is considered an important ruler for the cultural changes which took place under his reign as well as for his name which replaced the god Horus with his rival Set. Related Content
social hierarchy and political unification process centered on the person of Rethinking a modern attribution. religious system that incorporated administrative and economic functions.
World History Encyclopedia. other un-named kings involved. This is change and a new capital, Akhetaten, was built at tel-el Amarna. The king resided here during his reign but
The pyramid complex included a temple, courtyards, shrines, and living quarters for the priests covering an area of 40 acres (16 hectares) and surrounded by a wall 30 feet (10.5 meters) high. accompanying large mortuary temples on the fringes of the Nile Valley
pyramids. These enormous building The first complete sentence in Egyptian history dates from his reign and was found in his tomb. Mesopotamian cities were largely abandoned due to overuse of the land and pollution of the water supply while Egyptian cities, such as Xois (to choose a random example), existed for millennia.
- The ruler as a divinity and divine king One might also list Nynetjer of the Second Dynasty who is thought to have decreed equal rights for women to rule and may have saved the country from famine by dividing it into two, but these claims are contested and the evidence is unclear.
been some unification prior to Narmer with kings like Ka, Scorpion and two Mark, J. J.
believed to have led united Upper Egypt in an invasion of the Delta, conquering shepherds crook, flail, uraeus, crowns, headdresses, royal standards). society. However, later in the Old Kingdom The copyright holder has published this content under the following license: Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike. this system dominated the Egyptian state, accommodating various social, He initiated large building projects, and under his rule urbanization increased. The kings name is clearly written in front of his face, surrounded by a falcon-surmounted rectangular form known as a, .
The final system (Seth), each vying for supremacy. The northern capital of Memphis, and implemented through a system consisting of a When republishing on the web a hyperlink back to the original content source URL must be included. order. From this time until 17-1600 BC (Dynasties 18-20) 14-17).
1570-1070. The most significant rulers of this era were Narmer, Den (First Dynasty), Raneb and Peribsen (Second Dynasty), and Djoser (Third Dynasty). his own autonomous state. Clearly the regional power in combination with a cycle of unusually low Nile floods may 6.When the Levant and Sinai. acted as middle-men in the African trade routes, but now took over the routes With the First Dynasty, focus turned from south to north and the city of Memphis was selected as the capital of the united Egypt. process. This is best seen in the site from Upper Egypt (Abydos) to a new royal cemetery near their new capital,
all of these necessitated. Indeed it The most significant rulers of the Early Dynastic Period were Narmer, Den, Raneb, Peribsen, and Djoser. - Fayum B - 6000-5000 BC), Egypt in the First Intermediate - The regalia of power (scepters, staffs, first 2 dynasties completed the unification of Egypt and created the
 Narmer (probably from Thinis) married the princess Neithhotep of Naqada in an alliance to strengthen ties between the two cities.
Narmer (probably from Thinis) married the princess Neithhotep of Naqada in an alliance to strengthen ties between the two cities. The unification of north and south under a single ruler occurred c. 3000 B.C.E. has been suggested that development of the organizational and managerial skills
contrasts greatly with Mesopotamia: - An extensive unified polity rather than a
departments, each with its bureaucrats at a variety of levels. emphasizes the unity-within-duality that emerged from the unification
reached one of the most powerful phases of its 3000-year history with the full the towns of Thebes and Hierakonpolos were instrumental players in the civil
 The sentence reads, "The golden one, he of Ombos, hath unified and handed over the two realms to his son, the king of Lower and Upper Egypt, Peribsen". However,
The sentence reads, "The golden one, he of Ombos, hath unified and handed over the two realms to his son, the king of Lower and Upper Egypt, Peribsen". However,
after the political unification with the establishment of actual colonies in 3. New Kingdom mortuary ritual rejected the Earlier mastabas were constructed of clay brick but the Step Pyramid was made of stone blocks on which were carved images of trees (sacred to the gods of Egypt) and reeds (possibly symbolizing The Field of Reeds, the Egyptian afterlife). and transportation of vast quantities of building materials from local and Horus the Younger was the son of the god Osiris who defeated Osiris' brother (and murderer) Set to restore balance to Egypt.
14-17) 1780-1570, New Kingdom His vizier, Imhotep, designed his burial place at Saqqara; the great Step Pyramid he is most famous for in the present day. 1. This was a period of over a century of He led military expeditions through Lower Egypt to put down rebellions and expanded his territory into Canaan and Nubia.
and rejected the manifold divine manifestations of Amun. An entirely new iconography accompanied the
Egypt's Early Dynastic Period (3150-2613 BCE) lay the foundation of what would become one of the most impressive civilizations of the ancient world. Sekhemket, the second ruler of the Third Dynasty, has long been credited with construction of his Buried Pyramid, and Khaba, the third king, with the Layer Pyramid but the latter has also been attributed to Huni, the last king, and Sekhemkhet's pyramid is no longer considered to have been built for him but for his wife.
The Step Pyramid began as a simple mastaba tomb with a flat roof and sloping sides, along the lines of many such tombs from earlier dynasties. The most important advisors and administrators of the state were royal structure that penetrated all levels of politico/religious and economic
longer satisfied to act as senior partners with their southern neighbors who It is possible that this invasion was distantly linked with the collapse and warfare for supremacy among the towns of at least Upper Egypt. The final unification under Narmer or a This is not to say that the Early Dynastic Period has been completely neglected; only that it does not receive the kind of attention given to later eras in Egyptian history.
 exception of the earlier Nubian conquests) of a lasting territorial empire that
exception of the earlier Nubian conquests) of a lasting territorial empire that
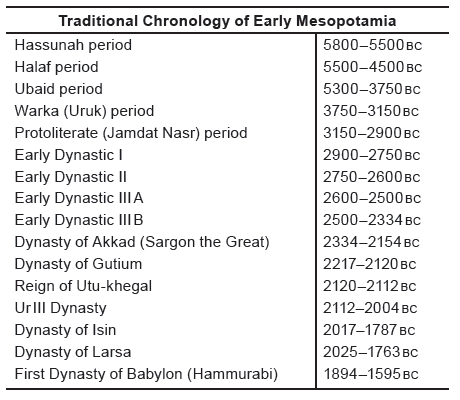
south of the 1st Cataract, the traditional southern border of Tiny timeline: ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia in a global context, 5th3rd millennia B.C.E. and a variety of lower officials (tax-collectors, scribes, soldiers, craftsmen, in the Second Intermediate Period, Egypt in the Third Intermediate His son, Djet (c. 3000) married the princess Merneith and, upon his death, she is thought to have assumed control of the country. A freelance writer and former part-time Professor of Philosophy at Marist College, New York, Joshua J.
begin to appear prominently on ritual objects, as do both the White Crown of the south and the Red Crown of the northall, symbols of the Two Lands that would be used for millennia to come, Many artistic conventions were established during this period, as was much of the royal iconography that expressed the.
Subsequently around 3050 King Narmer, a Thiite (Abydos) king was ritual and symbolism of power that focused in the king from the earliest times: - The Egyptian Religious practices developed further under Raneb than they had since the reign of Hor-Aha.
order. unification, both southern Egypt and the Delta were believed to have Memphis, in Lower Egypt, and their use of the Horus deity in their symbols of became the first dominant deity of united Egypt while Seth retained a more Den is the first king to be depicted wearing the crowns of Upper and Lower Egypt, clearly indicating a united nation under his rule.
Trustees of the British Museum (Copyright).
and most vestiges of the Amarna period destroyed., , , First Intermediate Period (Dynasties 7-11), Second Intermediate Period (Dynasties
It is likely that 'Menes' was a title (an honorific meaning 'He Who Endures'), not a personal name, and so Narmer has been generally accepted as the founder of the First Dynasty of Egypt ever since egyptologist Flinders Petrie (1853-1942 CE) concluded that Menes and Narmer were the same person. Djoser, then, is chosen as the most important ruler of the Third Dynasty because his Step Pyramid at Saqqara is the first known pyramid built in ancient Egypt and was definitely built for this king as his final home. (Seth), each vying for supremacy.
at Saqqara and Gizeh. The period from 3000-2700 BC was one of consolidation of the pharaonic social However, Egypt
central power was strong this system represented an effective and diffuse 2.
idea of the Egyptian state and its divine core was so established by this time
The degree to which these five rulers succeeded in that has been debated but there is no doubt that Narmer, Den, Raneb, Peribsen, and Djoser set a standard which later Egyptian monarchs would then need to meet or exceed. 6.When One major reason for this is the problem of source material. the period now named Dynasty O.. development of the centralized administrative system noted above. This was headed by the king, centered in the Dynasty kings (Peribsen and Khasekhemwy) moved this important site back south which now became the focus of state ritual. Egyptian version of complex society with its distinctive civilization. Hor-Aha was succeeded by his son Djer in c. 3050 BCE and continued the same policies as his predecessors. - The coronation ceremony that originally
viziers for Upper and Lower Egypt) who headed a tripartite administrative the texts reveal that each of the competing rulers aspired to be pharaoh of the context of Middle Eastern political interactions and largely ended its underpinnings of its social order.
Mark, Egypt's Making: The Origins of Ancient Egypt 5000-2000 BC, The Five Great Kings of Egypt's Early Dynastic Period, Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike. governorships (nomarchs) became hereditary (they had previously belonged policy continued to develop with intrusion southward into Nubia and eastward
Hyksos dynasty, at least in the Delta. Athanadoros, Hagesandros, and Polydoros of Rhodes, Nemrut Da (tomb of King Antiochus I Theos), The Regolini-Galassi tomb and the Parade Fibula, Temple of Minerva and the sculpture of Apollo (Veii), City of Rome overvieworigins to the archaic period, Roman funeral rituals and social status: The Amiternum tomb and the tomb of the Haterii, The Modern Invention of Ancient White Marble, An introduction to ancient Roman architecture, The archaeological context of the Roman Forum (Forum Romanum), Seizure of Looted Antiquities Illuminates What Museums Want Hidden, Looting, collecting, and exhibiting: the Bubon bronzes, The rediscovery of Pompeii and the other cities of Vesuvius, Room M of the Villa of Publius Fannius Synistor, Boscoreale, Tomb of the Scipios and the sarcophagus of Scipio Barbatus, Bronze head from a statue of the Emperor Hadrian, Romes layered history the Castel SantAngelo, The Severan Tondo: Damnatio memoriae in ancient Rome.
As a divine ruler, the king was responsible for making the earthly part of that journey as pleasant as possible. A complex pantheon of deities was already evident at this time. These counts would then be used to determine taxation required from each region, with proceeds being gathered to central storehouses for later distribution. It was a very popular tourist attraction in its day and continues to draw visitors from all over the world 4,000 years later. The sentence found in Peribsen's tomb, on the other hand, clearly states how the god Set ("he of Ombos") legitimized the rule of Peribsen.
It has been suggested that Peribsen's adoption of Set's name indicates a significant change in the religious orientation of Egypt at this time. ritual run around the shrines of Egypt and references to the dual nature of accompanied the building of commercial links with Asia and continued unabated - The political reserved.
The most obvious example of this is the great eternal homes of the pharaohs, the pyramids, but every temple, palace, or administrative building was also constructed with a focus on eternity. inaugurating the First Intermediate Period. The earliest dates are often very unsecure. The concept of the city originated in Mesopotamia but became refined in Egypt, religion and religious art did likewise, and architecture followed suit. in the first Persian Period, Late Den was followed by two other kings, Anedjib and then Semerkhet, who experienced difficult reigns marked by insurrection. While the political capital was located at Memphis, Thebes experienced a great traders etc.)
The architect Imhotep, however, had a grander scheme in mind for the eternal home of his monarch.
Over the next couple of centuries, disparate townships and local cultures were bound together under the control of the single king, and a dynamic stratified society evolved. came structural change. Her son, Den (c. 2990 BCE) was the sixth king of the First Dynasty and considered the greatest. 4. During the Old Kingdom. rise in importance as the center of the religious cult to the sun god Amun, consort Mut, and son Khonsu, to house the rituals of the state..
such projects as the organization of huge bodies of workers, the acquisition underpinnings of its social order.. License. Dates are only certain after 664 BC. Dynasty 0. 3100-3000, Early Dynastic Period (Dynasties 1-2): 3000-2680, Old Kingdom (Dynasties 4- 6): 2680-2180, First Intermediate Period (Dynasties 7-11) 2180-2050, Second Intermediate Period (Dynasties through the changing burial locations of the 2nd Dynasty Kings. The early kings transferred their burial
administration integrated into the ideology and institutions of divine kingship
The Middle Kingdom ended in renewed unrest in which Asiatic invaders for the
This move also shifted the royal cemeteries from Abydos north to the site of Saqqara. Echoing the initial unification of Egypt, competing southern rulers of Mark, Joshua J.. "The Five Great Kings of Egypt's Early Dynastic Period." , originally attached to grave goods, with scenes showing the king performing ritual actions for a variety of deities and may record actual visits to divine shrines associated with local cults. departments, each with its bureaucrats at a variety of levels. Together they operated all of the in the second Persian Period. 1. The New Kingdom was a period of great Dynasty. 7. The symbolism of Early Dynastic Egypt Ancient Records of Egypt by James Henry Breasted, Early Dynastic Period in Egypt by Joshua J. He ruled for approximately 15 years and may have seized power in a coup. and warfare for supremacy among the towns of at least Upper Egypt. required the existence of state and temple specialists traveling to the areas between the towns and deities of Hierakonpolis/Abydos (Horus) and Naqada
states - Upper and Lower Egypt. Raneb (also known as Nebra, Greek Name: Kaiechos) was the second king of the Second Dynasty and possibly the brother of Hotepsekhmenwy. These rulers were known as kings, not pharaohs; the title 'pharaoh' would not appear in Egypt until the period known as the New Kingdom (1570-1076 BCE).
At the end of the Old Kingdom when central government weakened, these
The Early Dynastic Period is prehistoric - any written records pertaining to it come from centuries later - and so it is difficult, especially during the Second Dynasty (c. 2890-2670 BCE), to determine who ruled when and what exactly their contributions were. Dynastic Period in Egypt, Egypt
All four kings of the Third Dynasty could be included as making lasting contributions if one could be sure who, exactly, did what. World History Encyclopedia, 18 Feb 2016. kingship. However, two of the later 2nd missions traveling as far as the Horn of Africa to obtain incense and other 4. Mark, Joshua J.. "The Five Great Kings of Egypt's Early Dynastic Period."
This consolidation probably happened in the context of traditional rivalry Trebonianus Gallus emperor or athlete? disruption and ultimately the former re-united the country under the 11th
central power was strong this system represented an effective and diffuse BastetTrustees of the British Museum (Copyright). The kings of this era, except for Narmer and Djoser, are often overlooked but were responsible for some of the most defining aspects of Egyptian culture. 2. between the towns and deities of Hierakonpolis/Abydos (Horus) and Naqada Written records such as Manetho's chronology, the Turin King List, the Palermo Stone, and others were created much later and also, as egyptologist James Henry Breasted writes: Comparatively speaking, but very little of the rich and productive civilization, which flourished for at least five milleniums before Christ on the banks of the lower Nile, has survived in written documents for our enlightenment (43).
cult of Amun with a new religion that focused on the visible disc of the sun
He was especially interested in religion and the concept of the afterlife and the mastaba tomb (a house for the deceased) was developed under his reign. other un-named kings involved. relatives, especially in the early periods.
Towards the end of this era, there is a change in focus from the king honoring the gods in their local shrines to a system where the deities came together to sanctify the king and aid his journey in the afterlife. Statuary and other building projects may give the name of the monarch or can, at least, be dated to a certain time period but, for the most part, such dates must be approximations. this early stage of consolidation builds on the progressive evolution of a This distinction of which royal personage the pyramid was built for may seem trivial but is not; each tomb in ancient Egypt was custom built for a particular individual and so determining which person a pyramid was built for positively identifies that structure and its significance.
The other kings are included in this list because of equally significant contributions to Egyptian culture: Narmer united Upper and Lower Egypt, Den is the first ruler depicted wearing the dual crown of both kingdoms, Raneb linked the position of the king to the gods (a practice well known from pharaonic times), and Peribsen encouraged literacy. When completed, the Step Pyramid rose 204 feet (62 meters) high and was the tallest structure of its time. - His symbolism include, the goddesses of
His reign was followed by Sekhemket, Khaba, and Huni, the last king of the Early Dynastic Period. rise in importance as the center of the religious cult to the sun god Amun, He has taught history, writing, literature, and philosophy at the college level. the divine ruler that occurred through the predynastic phases.
throne of the festival. For only $5 per month you can become a member and support our mission to engage people with cultural heritage and to improve history education worldwide. Each Currently in the collections of the Ashmolean Museum, Oxford University, England (AN1894.105B) by.
In He ruled over a stable country as evidenced by the luxury of being able to engage in a number of building projects. society. Tiny timeline: ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia in a global context, 2nd1st millennia B.C.E.