Spindle fibers are therefore an important and vital part of organisms and the cells that make them up. Spindle fibers are part of a spindle apparatus that moves chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis to ensure even chromosome distribution between daughter cells. Once we hit the telophase, the microtubules that are attached to the chromatids begin to disappear.  succeed. Microtubules are protein filaments that resemble hollow rods. Some of these microtubules will not attach to a chromosome and instead just help to push the cell apart. | Mitotic Spindle Formation & Role, Cell Division Stages, Process & Order | Cell Reproduction Stages. [38] In vivo polarity cues are determined by localization of Tricellular junctions localized at cell vertices. | A Guide to Summative Assessment, Public Speaking for Teachers: Professional Development, Supervision Principles for Teachers: Professional Development, Settlement of North America & the Colonies: Homeschool Curriculum, Quiz & Worksheet - Understanding Workers' Compensation, Quiz & Worksheet - Characteristics of Web 2.0, Quiz & Worksheet - Recission, Novation & Accord as Contract Discharge Options, Quiz & Worksheet - Rights of Creditors During Bankruptcies, Quiz & Worksheet - Photo Editing Software, Pope Gregory XII: Biography & Accomplishments, How to Study for AP Exam Free Response Questions at Home, Tech and Engineering - Questions & Answers, Health and Medicine - Questions & Answers. [27], Spindle assembly is largely regulated by phosphorylation events catalyzed by mitotic kinases. The unbound SAFs then promote microtubule nucleation and stabilization around mitotic chromatin, and spindle bipolarity is organized by microtubule motor proteins. - Definition, Function & Types, Cells With a Nucleus & Membrane-Bound Organelles, Cell-Free Protein Synthesis: Steps & Applications, Cells With & Without a Nucleus: Structure & Classification, Cellular Structure: Function & Definition, Pancreatic Acinar Cells: Definition & Function, DNA Replication - Processes and Steps: Help and Review, The Transcription and Translation Process: Help and Review, Plant Reproduction and Growth: Help and Review, Physiology I: The Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, and Musculoskeletal Systems, Physiology I - The Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, and Musculoskeletal Systems: Help and Review, Physiology II: The Nervous, Immune, and Endocrine Systems, Physiology II - The Nervous, Immune, and Endocrine Systems: Help and Review, Animal Reproduction and Development: Help and Review, Genetics - Principles of Heredity: Help and Review, The Origin and History of Life On Earth: Help and Review, Basic Molecular Biology Laboratory Techniques: Help and Review, High School Chemistry: Homework Help Resource, College Chemistry: Homework Help Resource, DSST Environmental Science: Study Guide & Test Prep, Introduction to Environmental Science: Certificate Program, Introduction to Natural Sciences: Certificate Program, CLEP Natural Sciences: Study Guide & Test Prep, DSST Health & Human Development: Study Guide & Test Prep, CSET Science Subtest I - General Science (215): Practice & Study Guide, ILTS Science - Chemistry (106): Test Practice and Study Guide, Mitotic Spindle: Definition, Formation & Function, TExES Science of Teaching Reading (293): Practice & Study Guide, Understanding the Scientific Methods for Research, Bliss by Katherine Mansfield: Characters & Quotes, Hemoglobin: Structure, Function & Impairment, John F. Kennedy's Accomplishments: Lesson for Kids, Evapotranspiration: Definition, Formula & Calculation, Henry Mintzberg & Organizational Structure, Quiz & Worksheet - The Death of Washington, Quiz & Worksheet - US Gang Violence Overview, Quiz & Worksheet - Aphorisms in The Importance of Being Earnest, Flashcards - Real Estate Marketing Basics, Flashcards - Promotional Marketing in Real Estate, What is Summative Assessment? This is so that there is a correct number of chromosomes within each nucleus of subsequent and resulting cells from each cell division process. Bailey, Regina. Acentrosomal or anastral spindles lack centrosomes or asters at the spindle poles, respectively, and occur for example during female meiosis in most animals. Spindle fibers are produced in the centrosome from cylindrical microtubules called centrioles. Spindle fibers function twice during meiosis. https://www.thoughtco.com/spindle-fibers-373548 (accessed July 22, 2022). Discover the part spindle fibers and cell division play in human growth. Spindle fibers take part in two kinds of cell division: meiosis and mitosis. [19][20] Such sliding forces may account not only for spindle pole separation early in mitosis, but also spindle elongation during late anaphase. CLIP170 was shown to localize near microtubule plus-ends in HeLa cells [7] and to accumulate in kinetochores during prometaphase. Meiosis is a cell division process that creates gametes or sex cells, and mitosis is a cell division process that creates replicated body cells. mitosis and meiosis. In order to understand why spindle fibers are important, it's important to first understand cell division in general, why organisms need it, and the two specific types of cell division. In animal cells, a mitotic spindle appears as asters that surround each centriole pair. Spindle fibers function similarly in meiosis, where four daughter cells are formed instead of two, by pulling homologous chromosomes apart after they have been duplicated to prepare for division. These nuclei then get divided into two separate cells during cytokinesis when the cytoplasm of the parent cell fully divides, completing the cell division. Constrained by cellular dimensions, lateral associations with antiparallel microtubules via motor proteins, and end-on attachments to kinetochores, microtubules naturally adopt a spindle-like structure with chromosomes aligned along the cell equator. An error occurred trying to load this video. Spindle fibers are found in eukaryotic cells and are a component of the cytoskeleton as well as cilia and flagella. Some of them attach to the kinetochores of the chromosomes while others bind to the arms of the chromosomes, still others continue to grow. [17], The activities of these MAPs are carefully regulated to maintain proper microtubule dynamics during spindle assembly, with many of these proteins serving as Aurora and Polo-like kinase substrates.[17][18].
succeed. Microtubules are protein filaments that resemble hollow rods. Some of these microtubules will not attach to a chromosome and instead just help to push the cell apart. | Mitotic Spindle Formation & Role, Cell Division Stages, Process & Order | Cell Reproduction Stages. [38] In vivo polarity cues are determined by localization of Tricellular junctions localized at cell vertices. | A Guide to Summative Assessment, Public Speaking for Teachers: Professional Development, Supervision Principles for Teachers: Professional Development, Settlement of North America & the Colonies: Homeschool Curriculum, Quiz & Worksheet - Understanding Workers' Compensation, Quiz & Worksheet - Characteristics of Web 2.0, Quiz & Worksheet - Recission, Novation & Accord as Contract Discharge Options, Quiz & Worksheet - Rights of Creditors During Bankruptcies, Quiz & Worksheet - Photo Editing Software, Pope Gregory XII: Biography & Accomplishments, How to Study for AP Exam Free Response Questions at Home, Tech and Engineering - Questions & Answers, Health and Medicine - Questions & Answers. [27], Spindle assembly is largely regulated by phosphorylation events catalyzed by mitotic kinases. The unbound SAFs then promote microtubule nucleation and stabilization around mitotic chromatin, and spindle bipolarity is organized by microtubule motor proteins. - Definition, Function & Types, Cells With a Nucleus & Membrane-Bound Organelles, Cell-Free Protein Synthesis: Steps & Applications, Cells With & Without a Nucleus: Structure & Classification, Cellular Structure: Function & Definition, Pancreatic Acinar Cells: Definition & Function, DNA Replication - Processes and Steps: Help and Review, The Transcription and Translation Process: Help and Review, Plant Reproduction and Growth: Help and Review, Physiology I: The Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, and Musculoskeletal Systems, Physiology I - The Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, and Musculoskeletal Systems: Help and Review, Physiology II: The Nervous, Immune, and Endocrine Systems, Physiology II - The Nervous, Immune, and Endocrine Systems: Help and Review, Animal Reproduction and Development: Help and Review, Genetics - Principles of Heredity: Help and Review, The Origin and History of Life On Earth: Help and Review, Basic Molecular Biology Laboratory Techniques: Help and Review, High School Chemistry: Homework Help Resource, College Chemistry: Homework Help Resource, DSST Environmental Science: Study Guide & Test Prep, Introduction to Environmental Science: Certificate Program, Introduction to Natural Sciences: Certificate Program, CLEP Natural Sciences: Study Guide & Test Prep, DSST Health & Human Development: Study Guide & Test Prep, CSET Science Subtest I - General Science (215): Practice & Study Guide, ILTS Science - Chemistry (106): Test Practice and Study Guide, Mitotic Spindle: Definition, Formation & Function, TExES Science of Teaching Reading (293): Practice & Study Guide, Understanding the Scientific Methods for Research, Bliss by Katherine Mansfield: Characters & Quotes, Hemoglobin: Structure, Function & Impairment, John F. Kennedy's Accomplishments: Lesson for Kids, Evapotranspiration: Definition, Formula & Calculation, Henry Mintzberg & Organizational Structure, Quiz & Worksheet - The Death of Washington, Quiz & Worksheet - US Gang Violence Overview, Quiz & Worksheet - Aphorisms in The Importance of Being Earnest, Flashcards - Real Estate Marketing Basics, Flashcards - Promotional Marketing in Real Estate, What is Summative Assessment? This is so that there is a correct number of chromosomes within each nucleus of subsequent and resulting cells from each cell division process. Bailey, Regina. Acentrosomal or anastral spindles lack centrosomes or asters at the spindle poles, respectively, and occur for example during female meiosis in most animals. Spindle fibers are produced in the centrosome from cylindrical microtubules called centrioles. Spindle fibers function twice during meiosis. https://www.thoughtco.com/spindle-fibers-373548 (accessed July 22, 2022). Discover the part spindle fibers and cell division play in human growth. Spindle fibers take part in two kinds of cell division: meiosis and mitosis. [19][20] Such sliding forces may account not only for spindle pole separation early in mitosis, but also spindle elongation during late anaphase. CLIP170 was shown to localize near microtubule plus-ends in HeLa cells [7] and to accumulate in kinetochores during prometaphase. Meiosis is a cell division process that creates gametes or sex cells, and mitosis is a cell division process that creates replicated body cells. mitosis and meiosis. In order to understand why spindle fibers are important, it's important to first understand cell division in general, why organisms need it, and the two specific types of cell division. In animal cells, a mitotic spindle appears as asters that surround each centriole pair. Spindle fibers function similarly in meiosis, where four daughter cells are formed instead of two, by pulling homologous chromosomes apart after they have been duplicated to prepare for division. These nuclei then get divided into two separate cells during cytokinesis when the cytoplasm of the parent cell fully divides, completing the cell division. Constrained by cellular dimensions, lateral associations with antiparallel microtubules via motor proteins, and end-on attachments to kinetochores, microtubules naturally adopt a spindle-like structure with chromosomes aligned along the cell equator. An error occurred trying to load this video. Spindle fibers are found in eukaryotic cells and are a component of the cytoskeleton as well as cilia and flagella. Some of them attach to the kinetochores of the chromosomes while others bind to the arms of the chromosomes, still others continue to grow. [17], The activities of these MAPs are carefully regulated to maintain proper microtubule dynamics during spindle assembly, with many of these proteins serving as Aurora and Polo-like kinase substrates.[17][18].
2012. Spindle fibers not connected to chromatids lengthen and elongate the cell to make room for the cell to separate. Once attached to opposite ends of a chromosome during metaphase, they contract, get smaller, and pull chromosomes apart toward opposite ends of the cell to ensure that divide cells get copies of the chromosomes. They move toward each centrosome, or as they are referred to now, spindle pole. Microtubule polymerization and depolymerization dynamic drive chromosome congression. Chromosome Condensation Overview & Levels | How is DNA Packaged? Cyclin dependent kinase complexes (CDKs) are activated by mitotic cyclins, whose translation increases during mitosis. Bailey, Regina. Attachment of microtubules to chromosomes is mediated by kinetochores, which actively monitor spindle formation and prevent premature anaphase onset. The content on this website is for information only. Spindle fibers are highly active during mitosis. [22] Indeed, it has also been shown that laser ablation of centrosomes in vertebrate cells inhibits neither spindle assembly nor chromosome segregation. Mesoderm Layer Function & Formation | What is a Mesoderm? Spindle fibers are aggregates of microtubules that move chromosomes during cell division. Meiosis I and mitosis consist of the same six to seven stages, depending on how you look at it. | Meiosis I Stages: Prophase, Anaphase, Metaphase & Telophase. [5] In this instance, a Ran GTP gradient is the main regulator of spindle microtubule organization and assembly. 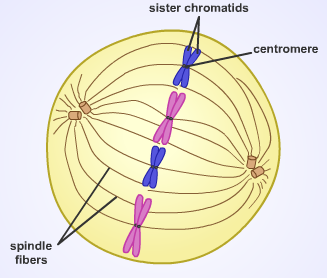 The microtubules that are not attached and are just still extended push the cell further from either end, and a small cleavage furrow or indentation appears as the cell goes through cytokinesis, or cytoplasm splitting. This process occurs again during meiosis II. Does the chromosomal microtubule from kinetochore and continuous microtubule from centriole combine to form the spindle fiber during cell division? In contrast to the search-and-capture mechanism in which centrosomes largely dictate the organization of the mitotic spindle, this model proposes that microtubules are nucleated acentrosomally near chromosomes and spontaneously assemble into anti-parallel bundles and adopt a spindle-like structure. Cell division is a process of a cell's life cycle that involves replicating its DNA and chromosomes before undergoing the division of its nucleus and the subsequent division of the cytoplasm. Microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) associate with microtubules at the midzone and the spindle poles to regulate their dynamics. [34] Experiments in Xenopus egg extracts have also implicated linker Histone H1 as an important regulator of mitotic chromosome compaction. A spindle fiber is composed of a microtubule extending from centrosomes. Spindle fiber and cell movement occur when microtubules and motor proteins interact. copyright 2003-2022 Study.com. There is interphase, prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and finally cytokinesis. "Spindle Fibers." We start off as a simple bundle of cells but are able to grow into rather complex individuals. In the wide middle portion, known as the spindle midzone, antiparallel microtubules are bundled by kinesins. Whereas, if spindle fibers fail during mitosis, the resulting body cells will be defective, may become cancerous, or will follow through with apoptosis and self-destruct to prevent further mistakes. Mitosis produces most of the other cells in the human body. Bailey, Regina. CDK1 (also called CDC2) is considered the main mitotic kinase in mammalian cells and is activated by Cyclin B1. As a member, you'll also get unlimited access to over 84,000 Spindle fibers are microtubules that extend from centrosomes in a cell and are cellular structures that form during and take part in the cell division of eukaryotic cells. In the search-and-capture model, the spindle is predominantly organized by the poleward separation of centrosomal microtubule organizing centers (MTOCs). Spindle fibers are a collective term for the centrosomes and microtubules that extend from them. Its like a teacher waved a magic wand and did the work for me. We've updated our Privacy Policy, which will go in to effect on September 1, 2022. In mitosis, these filaments form at opposite poles of the cell and meet at the equatorial plane. Any information here should not be considered absolutely correct, complete, and up-to-date.
The microtubules that are not attached and are just still extended push the cell further from either end, and a small cleavage furrow or indentation appears as the cell goes through cytokinesis, or cytoplasm splitting. This process occurs again during meiosis II. Does the chromosomal microtubule from kinetochore and continuous microtubule from centriole combine to form the spindle fiber during cell division? In contrast to the search-and-capture mechanism in which centrosomes largely dictate the organization of the mitotic spindle, this model proposes that microtubules are nucleated acentrosomally near chromosomes and spontaneously assemble into anti-parallel bundles and adopt a spindle-like structure. Cell division is a process of a cell's life cycle that involves replicating its DNA and chromosomes before undergoing the division of its nucleus and the subsequent division of the cytoplasm. Microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) associate with microtubules at the midzone and the spindle poles to regulate their dynamics. [34] Experiments in Xenopus egg extracts have also implicated linker Histone H1 as an important regulator of mitotic chromosome compaction. A spindle fiber is composed of a microtubule extending from centrosomes. Spindle fiber and cell movement occur when microtubules and motor proteins interact. copyright 2003-2022 Study.com. There is interphase, prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and finally cytokinesis. "Spindle Fibers." We start off as a simple bundle of cells but are able to grow into rather complex individuals. In the wide middle portion, known as the spindle midzone, antiparallel microtubules are bundled by kinesins. Whereas, if spindle fibers fail during mitosis, the resulting body cells will be defective, may become cancerous, or will follow through with apoptosis and self-destruct to prevent further mistakes. Mitosis produces most of the other cells in the human body. Bailey, Regina. CDK1 (also called CDC2) is considered the main mitotic kinase in mammalian cells and is activated by Cyclin B1. As a member, you'll also get unlimited access to over 84,000 Spindle fibers are microtubules that extend from centrosomes in a cell and are cellular structures that form during and take part in the cell division of eukaryotic cells. In the search-and-capture model, the spindle is predominantly organized by the poleward separation of centrosomal microtubule organizing centers (MTOCs). Spindle fibers are a collective term for the centrosomes and microtubules that extend from them. Its like a teacher waved a magic wand and did the work for me. We've updated our Privacy Policy, which will go in to effect on September 1, 2022. In mitosis, these filaments form at opposite poles of the cell and meet at the equatorial plane. Any information here should not be considered absolutely correct, complete, and up-to-date.
 During anaphase II, the chromatids are split apart toward opposite ends of the cell where they again reform nuclei around them. As the cell begins the prometaphase stage, the centrosomes with microtubules move to opposite sides of the cell.
During anaphase II, the chromatids are split apart toward opposite ends of the cell where they again reform nuclei around them. As the cell begins the prometaphase stage, the centrosomes with microtubules move to opposite sides of the cell.
Cells replicate so that the organisms they make up can grow, mature, and heal when necessary. Views expressed here do not necessarily reflect those of Biology Online, its staff, or its partners. Spindle fibers can collectively be considered a number of different fibers and tubules inside of the cell.
Two models predominate the field, which are synergistic and not mutually exclusive. Are kinetochores part of the spindle apparatus? Mitotic entry triggers a dramatic reorganization of the duplicated genome, resulting in sister chromatids that are disentangled and separated from one another. As we go into greater detail as to what these terms are and how spindle fibers are important, you'll notice that spindle fibers are used as a collective term and encompass some more specific terminology. [15] Additional microtubule destabilizing proteins include Op18/stathmin and katanin which have roles in remodeling the mitotic spindle as well as promoting chromosome segregation during anaphase. Spindle fibers are necessary during both cell division processes of mitosis and meiosis. [35], The completion of spindle formation is a crucial transition point in the cell cycle called the spindle assembly checkpoint. These fibers overlap and push cell poles away from one another in preparation for cytokinesis. This second attachment further stabilizes kinetochore attachment to the mitotic spindle. Though the cell completes PMAT twice, each process is slightly different. Specifically, spindle fibers fulfill their purpose during the metaphases and anaphases of both mitosis and meiosis. [30][31][32], While these dynamic rearrangements are vitally important to ensure accurate and high-fidelity segregation of the genome, our understanding of mitotic chromosome structure remains largely incomplete. Spindle microtubules emanate from centrosomes and 'seek' out kinetochores; when they bind a kinetochore they become stabilized and exert tension on the chromosomes. I feel like its a lifeline. First, when do spindle fibers form during the cell division process? Variant: spindle fibre See also: Muscle cells are specialized to generate force and movement. Spindle fibers work by growing toward chromosomes lined up in the middle of a cell during metaphase of either mitosis or meiosis. This gives mitotic chromosomes the classic X shape seen in karyotypes, with each condensed sister chromatid linked along their lengths by cohesin proteins and joined, often near the center, at the centromere. Aurora B is a member of the chromosomal passenger complex and mediates chromosome-microtubule attachment and sister chromatid cohesion. If both instances of PMAT are not undergone correctly, and a gamete ends up with an incorrect number of chromosomes, this can lead to genetic and birth defects within the offspring. 18, 449-485. -tubulin is a specialized tubulin variant that assembles into a ring complex called -TuRC which nucleates polymerization of / tubulin heterodimers into microtubules. Anaphase: Spindle fibers shorten and pullsister chromatids toward spindle poles.
Morgan DO: The Cell Cycle: Principles of Control (Primers inBiology) London: New Science Press Ltd; 2007:297. [36] Failure of this spindle assembly checkpoint can result in aneuploidy and may be involved in aging and the formation of cancer.[37].
[6], The growing ends of microtubules are protected against catastrophe by the action of plus-end microtubule tracking proteins (+TIPs) to promote their association with kinetochores at the midzone. In this model, microtubules are nucleated at microtubule organizing centers and undergo rapid growth and catastrophe to 'search' the cytoplasm for kinetochores.
Microtubules that form the spindle fibers come from centrosomes, which are organelles located in opposite poles near the nucleus. A Genetics Definition of Homologous Chromosomes, Role of a Kinetochore During Cell Division, Microtubules, the Structural Foundation of Your Cells. Endocardium Overview, Parts & Function | What is the Endocardium? Her work has been featured in "Kaplan AP Biology" and "The Internet for Cellular and Molecular Biologists.". Prophase: Spindle fibers form at opposite poles of the cell. For ease of explanation, I will refer to them as just 'cell division.' Mitosis is another cell division process that spindle fibers take part in. What is the function of aster and spindle fibers? This makes each gamete genetically unique from one another and therefore results in variations amongst offspring that were sexually reproduced by the same parents. Microtubules are polymers of alpha- and beta-tubulin dimers. The microtubule-associated protein Augmin acts in conjunction with -TURC to nucleate new microtubules off of existing microtubules. Spindle fibers are microtubules extending from the centrosomes within a cell. During the process of meiosis, a single gamete-producing cell divides twice in order to produce four gametes. {{courseNav.course.mDynamicIntFields.lessonCount}} lessons Motor proteins such as dyneins and kinesins move along microtubules whose fibers either lengthen or shorten. The purpose of cell division is the replication of a cell. Spindle fibers move chromosomes during cell division by attaching to chromosome arms and centromeres. Joseph Comunale obtained a Bachelor's in Philosophy from UCF before becoming a high school science teacher for five years. They extend out microtubules that are used to pull the chromosomes (condensed DNA pairs) apart and to each side of the cell, allowing the two daughter cells to be completely identical. Recruitment of -TuRC to the pericentrosomal region stabilizes microtubule minus-ends and anchors them near the microtubule-organizing center. But exactly what is the role of the spindle fibers? Both gametes combine and form a zygote, or fertilized egg which is a diploid cell that contains the full and correct number of chromosomes. Telophase: Spindle fibers disperse as the chromosomes are separated and become housed within two new nuclei. They start to look something like a spider with lots of legs. However, during prophase I of meiosis I, duplicated sets of homologous chromosomes pair up into tetrads forming a "XX" structure seen in the above diagram. They are chiefly involved in moving and segregating the chromosomes during nuclear division. This contributes to further genetic diversity by creating new allele combinations within the chromosomes. It is here that they will stay and their microtubules will go to work. They form and exist through nearly all of the different phases. Each of the gametes contains a random half of the alleles or options for each gene contained by the parent cell.
[24], The guanine nucleotide exchange factor for the small GTPase Ran (Regulator of chromosome condensation 1 or RCC1) is attached to nucleosomes via core histones H2A and H2B. Spindle fibers are absolutely vital in ensuring that the correct number of homologous chromosomes or duplicated chromosomes end up on opposite ends of the cell. Spindle fibers become visible during the first stage of any cell division process known as prophase. Fingernail Parts & Function | What are Fingernails Made of? It is important for each spindle fiber to attach to a chromatid correctly for the next part of the process. This diagram shows the spindle fibers function within mitosis. I would definitely recommend Study.com to my colleagues. The cytoplasm divides and the distinct daughter cells fully separate. Each microtubule will attach to one half of the chromosome called a chromatid. What is the role of the spindle fibers during mitosis? Cells tend to divide along their long axis according to the so-called Hertwig rule. If chromosomes are not properly attached to the mitotic spindle by the time of this checkpoint, the onset of anaphase will be delayed. [23] Under this scheme, the shape and size of the mitotic spindle are a function of the biophysical properties of the cross-linking motor proteins. Genetic Linkage Concept & Analysis | What is Genetic Linkage? Meiosis is a cell division process that is undergone by gamete-producing cells, or cells that divide into sex cells like sperm or eggs for the purpose of sexual reproduction. | {{course.flashcardSetCount}} Before using our website, please read our Privacy Policy. Spindle fibers are made up of microtubules. Mitosis is specifically the division of a body cell's nucleus into two separate nuclei at the end of mitosis. They are responsible for organizing packages of DNA (chromosomes) on opposite ends of a cell to ensure that duplicated nuclei can divide into subsequent cells. [12] Plus-end polymerization may be further moderated by the EB1 protein, which directly binds the growing ends of microtubules and coordinates the binding of other +TIPs. The cell's centrosomes - small organelles that organize and arrange the microtubules - begin to form microtubules. "Spindle Fibers." During anaphase, the spindle fibers then pull apart the duplicated chromosomes so that their sister chromatids are separated to opposite ends of the cell. The precise orientation of this complex is required to ensure accurate chromosome segregation and to specify the cell division plane. This time the spindle fibers attach to opposite chromatids that make up the same chromosomes.