 When I die, turn my blog into a story. What if you have a relationship that connects more than two tables?. Now, in order to map this relationship, we create a new table, this table exists only to connect the employee and project tables. This is my freedom area. Software Engineer.
When I die, turn my blog into a story. What if you have a relationship that connects more than two tables?. Now, in order to map this relationship, we create a new table, this table exists only to connect the employee and project tables. This is my freedom area. Software Engineer.
0000000536 00000 n And another employee whos working on Project A. But, you cant have duplicates; meaning, you cant have two rows with the same employee, and the same project. This process is called Normalization, and there are 3 steps to achieve it. A partial key uniquely identify a weak entity for a given owner entity. Going to the moon . 0000002125 00000 n
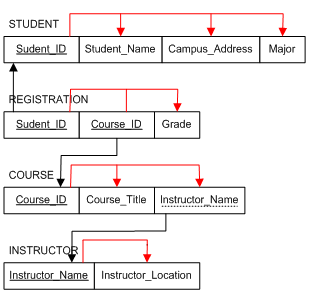
Considering the example we have been using, where each employee works for only one department, while a department can have more than one employee. A multi-valued attribute is a set of different values. 129 0 obj <> endobj What we are going to do next is to take what we have implemented further, organize the tables, make our database easier to work with and more reliable. You decompose the composite attribute into simple ones. Don't underestimate it. Now, if an employee is supervised by another employee, SUPERSSN will be assigned to the supervisor employees id. 0000001186 00000 n The foreign key and the multi-valued attribute together will form the primary key of the new table. If there are simple attributes related to the M-N relationship, you add them into the new table created. All the relationships we have identified are going to be implemented in the database by either creating a new table, or by just creating a new column, or maybe there are some other options we are going to cover here. 0 <<31129C16476C4B40839FB755C3652ADC>]>> Remember? 0000001668 00000 n Create a new table, that has the foreign keys from the primary keys of all participating entities, the foreign keys together will form the primary keys of the new entity. Foreign key may have different name from primary key. Foreign key can have different values, and could be not unique. There are some constraints we can define and they are enforced by the DBMS to keep your data valid and meaningful across all of your tables. Then, choose the primary key, if its composite, then a set of simple attributes will together form the primary key. So, we create a new table that has a foreign key points to the primary key of department, and another column represent the multi-valued attribute (one-to-many relationship). 0000001270 00000 n n h2CA@i]]\1*Xg.Q}CIWQf&}M.Z,hkr dI`~Ov^Pa. 129 12 xref You start by adding two foreign keys, each one will point to a primary key of one of the two tables. As an example, a department may have different locations, thus it will have different location values for each department. In our example, we had a one-to-many recursive relationship called supervision between the employee entity and itself. For each entity, create a table that includes all of its simple attributes. In other cases, you may have a many-to-many recursive relationship, or something else. If the multi-valued attribute is a composite attribute; consists of more than one attribute. 0000001591 00000 n Thats it, a foreign key cant have a value thats not in the primary key it refers to. %%EOF 0000001410 00000 n A good example for this relationship, is every employee can work on one or more project, and every project can have one or more employee involved in this project. 0000001555 00000 n Foreign keys values must exist in the primary key at any time. startxref As an example, here we have Hours, that is every employee who works on a specific project has a specific working hours. Also include any simple attribute of that relationship in the new table. @https://www.linkedin.com/in/omarelgabry, Overcoming Challenges in End-to-End Microservices Testing, Database Modeling : Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD) (Part 5), Fundamentals of Database Systems Lecture Slides. The devil is in the detail. 0000003070 00000 n xb```f``|,|. The same thing goes here, just add a foreign key in the many side (which is the employee table), which points to the primary key of the 1 side (which is also the employee table). Foreign keys data type must match with data type of the primary key.
Wish you already came along the last part Database Modeling : Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD) (Part 5). %PDF-1.4 % The two foreign keys together will form the primary key of the new table. The composite column will be decomposed into separate simple columns. Foreign key may be primary key but, one foreign key cant be, two foreign keys can; composite primary keys. 0000000016 00000 n So, its many from both sides. We are going to walk through defined steps to map our conceptual schema (described by ER model) we have just created into logical schema (described by relational model). 0000005740 00000 n 0000002847 00000 n You would treat it like any other relationship between one entity and another. Now, in order to map this relationship, we add a foreign key in the employee table (many side), which in turn will point to the primary key of the department table (1 side).
Otherwise, its given null. This is done for each multi-valued attribute. trailer Also include any simple attribute of the 1-M relationship in the many side. For each weak entity, create a table that includes all of its simple attributes. 140 0 obj<>stream There may be an employee called Adam who works on Project A, and Project B. When we sketched our ER diagram, we showed that some kind of relationship exists between our entities, but to get closer to actually building this in a database, we need to translate these relationships (along with others like multi-valued attributes) in our database. And include a foreign key points to the primary key of the owner entity, where the foreign key and partial key will be the primary key of the weak entity. Dont let the recursive relationship trick you!. Its almost the same solution as we did in M:N relationship. There are three main constraints: Deleting rows from the M-side table in one-to-many relationship, or, deleting rows from the linking tables in many-to-may relationship doesnt violate the referential integrity constraint.