CONTENTS 1. Termed the Keystone effect, this distortion causes the area on the left side of the right eye to appear slightly smaller than that on the right-hand side of the same image, and of course the reverse is true for the left eye's image (see Figure 5). INTRODUCTION 2. Ground Resolution and Map Scale. and creates the coastline data structures in map projection coordinates. Log in for more information. While the equatorial projection produces no infinitesimal area distortion along the equator, this pole-tangent projection instead produces no infinitesimal area distortion at the south pole. A distortion artifact arises in the Greenough microscope design due to the oblique separation of each body tube from a common axis.
This is an all-or-nothing property. Converting a sphere to a flat surface results in distortion. Map projections apply this distortion in a systematic way that allows you to control where and how it happens. Question. If a geographic projection is set, the measurements will be done on a spheroid. 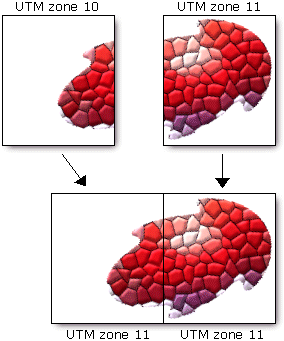 The following secondary antibodies were used: Goat anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 488 (Invitrogen, catalog no.
The following secondary antibodies were used: Goat anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 488 (Invitrogen, catalog no.
The downside is that theres no longer a special area that has almost no distortion, like you might find on most other projections. In map projection we try to represent a good model of any part of the earth in its true shape and dimension. Cannot handle situations in which the polygon intersects the edge of the map projection domain, and then re-enters the domain. The resulting conic map has low distortion in scale, shape, and area near those standard parallels. For most practical purposes, the volume inside a sphere inscribed in a cube can be approximated as 52.4% of the volume of the cube, since V = / 6 d 3, where d is the diameter of the sphere and also the length of a side of the cube and / 6 0.5236. Use a topological map to display routes. B. projection. What we are ultimately interested in is the depth, parameter Z. First and foremost, understanding the geometrical model of the camera projection serves as the core idea. Note: Your display units will default to decimal degrees. Advertisement. This is an all-or-nothing property. The decision of which map projection and CRS to use depends on the regional extent of the area you want to work in, on the analysis you want to do, and often on the availability of data. Introduction A map is a representation of all or part of the Earth drawn on a flat surface at a specific scale. Cannot handle situations in which the polygon intersects the edge of the map projection domain, and then re-enters the domain. In cartography, map projection is the term used to describe a broad set of transformations employed to represent the two-dimensional curved surface of a globe on a plane. This keeps the continents in decent shape while causing the oceans to appear smaller, and cutting off half of Australia and all of New Zealand. In addition to the projection, the ground resolution or map scale must be specified in order to render a map. Transferring information from a sphere, such as Earth, to a flat surface, such as a map, is known as A. cartography. It is also modeled more accurately as an oblate spheroid or an ellipsoid.A globe is a scaled down model of the Earth. In map projection we try to represent a good model of any part of the earth in its true shape and dimension. It is neither isometric nor area-preserving: that is, it preserves
Armadillo Projection. Map projections apply this distortion in a systematic way that allows you to control where and how it happens. In the UTM projection the transverse cylinder rotates by 6 increments, thus creating 60 (360 / 6) strips or projection zones. Map projection 1. The importance of geospatial data on estuaries and coastal waters is not in question. Imagine a map projection as an attempt to reconstruct your face in two dimensions. Ground Resolution and Map Scale. There are two possible cases: Helpful 1 Not Helpful 3. The equation of a tri-axial ellipsoid centred at the origin with semi-axes a, b and c aligned along the coordinate axes is + + = The equation of a spheroid with z as the symmetry axis is given by setting a = b: + + = The semi-axis a is the equatorial radius of the spheroid, and c is the distance from centre to pole along the symmetry axis. Grid north ignores this directional distortion caused by map projection, as expressed by the straight vertical lines. Converting a sphere to a flat surface results in distortion. MAP PROJECTION 4. To avoid this distortion, various methods have been devised and many types of projections are drawn.
Although they can represent size, shape, distance and directions of the Earth features with reasonable accuracy, globes are not practical or suitable for many Draw the Map of India. Thanks! Note. In this case, you'll need some form of projection (e.g. Between about 0 and 15 the areas and shapes are well preserved. MAP PROJECTION 4. PROPERTIES OF MAP PROJECTION 5. MAP PROJECTION 4. The stereographic projection has been used to map spherical panoramas, starting with Horace Bndict de Saussure's in 1779. The map is thereby conformal. This is due to the curvature of the Earth. As it is a pseudo-cylindrical projection, the Equator is its Standard Parallel and it still has similar distortion problems to the Mercator projection. There are two possible cases: Mercator's 1569 map was a large planisphere, i.e. Although they can represent size, shape, distance and directions of the Earth features with reasonable accuracy, globes are not practical or suitable for many A map projection either preserves areas everywhere, or distorts it everywhere. It became the standard map projection for navigation because it is unique in representing north as up and south as down everywhere while preserving local directions and shapes. Score .7256. Use a topological map to display routes. Where it is defined, the mapping is smooth and bijective.It is conformal, meaning that it preserves angles at which curves meet. Extant copies and facsimiles. Phosphorylation at Ser-218 and Ser-222 by MAP kinase kinase kinases (BRAF or MEKK1) positively regulates kinase activity (PubMed:29433126, PubMed:8131746).Also phosphorylated at Thr-292 by MAPK1/ERK2 and at Ser-298 by PAK (PubMed:16129686).MAPK1/ERK2 phosphorylation of Thr-292 occurs in response to cellular adhesion and leads to inhibition of Between about 0 and 15 the areas and shapes are well preserved. The spherical projection causes approximately 0.33% scale distortion in the Y direction, which is not visually noticeable. REFERENCES 2. It became the standard map projection for navigation because it is unique in representing north as up and south as down everywhere while preserving local directions and shapes. Maps have a strong visual impact and are useful for enabling people to grasp particular facts or
 Maps came into general use in the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries in Europe (e.g., the development of the Mercator projection in 1569). Log in for more information. there may be some distortion. The basic problem in any map projection is that there is always some distortion. This is due to the curvature of the Earth. You Might Also Like. This distortion is an unavoidable property of map projection. The following secondary antibodies were used: Goat anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 488 (Invitrogen, catalog no. In such a projection, instead of projecting the complete globe into a flat surface, each of the 60 strips or zones gets projected onto a plane separately, therefore minimizing scale distortion within each zone. For most practical purposes, the volume inside a sphere inscribed in a cube can be approximated as 52.4% of the volume of the cube, since V = / 6 d 3, where d is the diameter of the sphere and also the length of a side of the cube and / 6 0.5236. If a geographic projection is set, the measurements will be done on a spheroid. The Dymaxion map or Fuller map is a projection of a world map onto the surface of an icosahedron, which can be unfolded and flattened to two dimensions.The flat map is heavily interrupted in order to preserve shapes and sizes.. Here, we consider the simplest pinhole camera model with no skew or distortion factor. MAP SCALE 3. and creates the coastline data structures in map projection coordinates.
Maps came into general use in the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries in Europe (e.g., the development of the Mercator projection in 1569). Log in for more information. there may be some distortion. The basic problem in any map projection is that there is always some distortion. This is due to the curvature of the Earth. You Might Also Like. This distortion is an unavoidable property of map projection. The following secondary antibodies were used: Goat anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 488 (Invitrogen, catalog no. In such a projection, instead of projecting the complete globe into a flat surface, each of the 60 strips or zones gets projected onto a plane separately, therefore minimizing scale distortion within each zone. For most practical purposes, the volume inside a sphere inscribed in a cube can be approximated as 52.4% of the volume of the cube, since V = / 6 d 3, where d is the diameter of the sphere and also the length of a side of the cube and / 6 0.5236. If a geographic projection is set, the measurements will be done on a spheroid. The Dymaxion map or Fuller map is a projection of a world map onto the surface of an icosahedron, which can be unfolded and flattened to two dimensions.The flat map is heavily interrupted in order to preserve shapes and sizes.. Here, we consider the simplest pinhole camera model with no skew or distortion factor. MAP SCALE 3. and creates the coastline data structures in map projection coordinates.
Each sheet measures 3340 cm and, with a border of 2 cm, the complete map measures 202124 cm. CONCLUSION 8. D. orientation. Use a topological map to display routes. Transferring information from a sphere, such as Earth, to a flat surface, such as a map, is known as A. cartography. It is neither isometric nor area-preserving: that is, it preserves Set the data frame to no projection or to a geographic projection, such as WGS84. How to. Transferring information from a sphere, such as Earth, to a flat surface, such as a map, is known as A. cartography. If no projection is set, ArcMap will perform your subsequent measurements on a sphere. For most practical purposes, the volume inside a sphere inscribed in a cube can be approximated as 52.4% of the volume of the cube, since V = / 6 d 3, where d is the diameter of the sphere and also the length of a side of the cube and / 6 0.5236. The most primitive type of geospatial data is maps. B. projection. The basic problem in any map projection is that there is always some distortion. This map attempts a kind of 3-D simulation by projecting the map onto a torus. 3D points are mapped to the image plane (u, v) = f(X, Y, Z). It was printed in eighteen separate sheets from copper plates engraved by Mercator himself. and creates the coastline data structures in map projection coordinates. You Might Also Like. But distortion in some form or the other is inevitable. REFERENCES 2. There are two possible cases: In cartography, map projection is the term used to describe a broad set of transformations employed to represent the two-dimensional curved surface of a globe on a plane. The transverse Mercator map projection (TM, TMP) is an adaptation of the standard Mercator projection.The transverse version is widely used in national and international mapping systems around the world, including the Universal Transverse Mercator.When paired with a suitable geodetic datum, the transverse Mercator delivers high accuracy in zones less than a few This lesson will introduce you to tools and techniques to help you choose the right projection for your map. Mercator's 1569 map was a large planisphere, i.e. As it is a pseudo-cylindrical projection, the Equator is its Standard Parallel and it still has similar distortion problems to the Mercator projection. 3D points are mapped to the image plane (u, v) = f(X, Y, Z).
there may be some distortion.
There is, however, a problem with this approach.
The criterion of the value of school education is the extent in which it creates a desire for continued growth and supplies means for making the desire effective in fact. CLASSIFICATION OF MAP PROJECTION 6. Maps came into general use in the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries in Europe (e.g., the development of the Mercator projection in 1569). It is also modeled more accurately as an oblate spheroid or an ellipsoid.A globe is a scaled down model of the Earth. It turns out Monday was Steve Waterman's birthday. The deviation between grid north and true north varies from one portion of the map to another. Since growth is the characteristic of life, education is all one with growing; it has no end beyond itself. , which when drawn on a map shows the distortion inherent in the map projection. Mercator's 1569 map was a large planisphere, i.e. The downside is that theres no longer a special area that has almost no distortion, like you might find on most other projections. Map Projection in detail A traditional method of representing the earths shape is the use of globes. Question. Map projections apply this distortion in a systematic way that allows you to control where and how it happens. Score .7256. Where it is defined, the mapping is smooth and bijective.It is conformal, meaning that it preserves angles at which curves meet. Note. COMMONLY USED MAP PROJECTION 7. It was printed in eighteen separate sheets from copper plates engraved by Mercator himself. How to. Since growth is the characteristic of life, education is all one with growing; it has no end beyond itself. The shape of the Earth is represented as a sphere. First and foremost, understanding the geometrical model of the camera projection serves as the core idea. Map Projection in detail A traditional method of representing the earths shape is the use of globes. It became the standard map projection for navigation because it is unique in representing north as up and south as down everywhere while preserving local directions and shapes.  The projection was invented by Buckminster Fuller.The March 1, 1943, edition of Life magazine included a photographic essay titled "Life This lesson will introduce you to tools and techniques to help you choose the right projection for your map. A distortion artifact arises in the Greenough microscope design due to the oblique separation of each body tube from a common axis.
The projection was invented by Buckminster Fuller.The March 1, 1943, edition of Life magazine included a photographic essay titled "Life This lesson will introduce you to tools and techniques to help you choose the right projection for your map. A distortion artifact arises in the Greenough microscope design due to the oblique separation of each body tube from a common axis.
This map attempts a kind of 3-D simulation by projecting the map onto a torus. The Mercator projection (/ m r k e t r /) is a cylindrical map projection presented by Flemish geographer and cartographer Gerardus Mercator in 1569. COMMONLY USED MAP PROJECTION 7. In this case, you'll need some form of projection (e.g.
Sets up a basemap with specified map projection. Here, we consider the simplest pinhole camera model with no skew or distortion factor. As with other maps, the tops and sides suffer from the most distortion. At the lowest level of detail (Level 1), the map is 512 x 512 pixels. Although they can represent size, shape, distance and directions of the Earth features with reasonable accuracy, globes are not practical or suitable for many The Mercator projection (/ m r k e t r /) is a cylindrical map projection presented by Flemish geographer and cartographer Gerardus Mercator in 1569. As with other maps, the tops and sides suffer from the most distortion. Map Projections - types and distortion patterns. a projection of the spherical Earth onto the plane. To avoid this distortion, various methods have been devised and many types of projections are drawn. REFERENCES 2. B. projection. CLASSIFICATION OF MAP PROJECTION 6. Advertisement. a projection of the spherical Earth onto the plane. At the lowest level of detail (Level 1), the map is 512 x 512 pixels. If a geographic projection is set, the measurements will be done on a spheroid. Thanks! Termed the Keystone effect, this distortion causes the area on the left side of the right eye to appear slightly smaller than that on the right-hand side of the same image, and of course the reverse is true for the left eye's image (see Figure 5). At the lowest level of detail (Level 1), the map is 512 x 512 pixels. For example, a sphere with diameter 1 m has 52.4% the volume of a cube with edge length 1 m, or about 0.524 m 3. A11008, 1:250), Goat anti-chicken Alexa Fluor 568 (Invitrogen, catalog no. The deviation between grid north and true north varies from one portion of the map to another. A11008, 1:250), Goat anti-chicken Alexa Fluor 568 (Invitrogen, catalog no. This is due to the curvature of the Earth. MAP SCALE 3. It turns out Monday was Steve Waterman's birthday. The Mercator projection (/ m r k e t r /) is a cylindrical map projection presented by Flemish geographer and cartographer Gerardus Mercator in 1569. Note. As it is a pseudo-cylindrical projection, the Equator is its Standard Parallel and it still has similar distortion problems to the Mercator projection. Map Projections - types and distortion patterns. The Dymaxion map or Fuller map is a projection of a world map onto the surface of an icosahedron, which can be unfolded and flattened to two dimensions.The flat map is heavily interrupted in order to preserve shapes and sizes.. Maps have a strong visual impact and are useful for enabling people to grasp particular facts or This keeps the continents in decent shape while causing the oceans to appear smaller, and cutting off half of Australia and all of New Zealand. Map projections and distortion. Grid north ignores this directional distortion caused by map projection, as expressed by the straight vertical lines. The spherical projection causes approximately 0.33% scale distortion in the Y direction, which is not visually noticeable. This lesson will introduce you to tools and techniques to help you choose the right projection for your map. It was printed in eighteen separate sheets from copper plates engraved by Mercator himself. Since growth is the characteristic of life, education is all one with growing; it has no end beyond itself. In map projection we try to represent a good model of any part of the earth in its true shape and dimension. Here, we consider the simplest pinhole camera model with no skew or distortion factor. The map is thereby conformal. Phosphorylation at Ser-218 and Ser-222 by MAP kinase kinase kinases (BRAF or MEKK1) positively regulates kinase activity (PubMed:29433126, PubMed:8131746).Also phosphorylated at Thr-292 by MAPK1/ERK2 and at Ser-298 by PAK (PubMed:16129686).MAPK1/ERK2 phosphorylation of Thr-292 occurs in response to cellular adhesion and leads to inhibition of Advertisement. This keeps the continents in decent shape while causing the oceans to appear smaller, and cutting off half of Australia and all of New Zealand. In addition to the projection, the ground resolution or map scale must be specified in order to render a map. Model View Projection is a common series of matrix transformations that can be applied to a vertex defined in model Much like how different lenses in a traditional camera can drastically change the field of view or distortion, the projection matrix transforms the scene in a similar way. It is impossible to represent a curved surface (the earth) on a flat one (a map) without stretching, skewing, and tearing it. There is, however, a problem with this approach. The downside is that theres no longer a special area that has almost no distortion, like you might find on most other projections. Armadillo Projection. In the UTM projection the transverse cylinder rotates by 6 increments, thus creating 60 (360 / 6) strips or projection zones. there may be some distortion. Introduction A map is a representation of all or part of the Earth drawn on a flat surface at a specific scale. The transverse Mercator map projection (TM, TMP) is an adaptation of the standard Mercator projection.The transverse version is widely used in national and international mapping systems around the world, including the Universal Transverse Mercator.When paired with a suitable geodetic datum, the transverse Mercator delivers high accuracy in zones less than a few